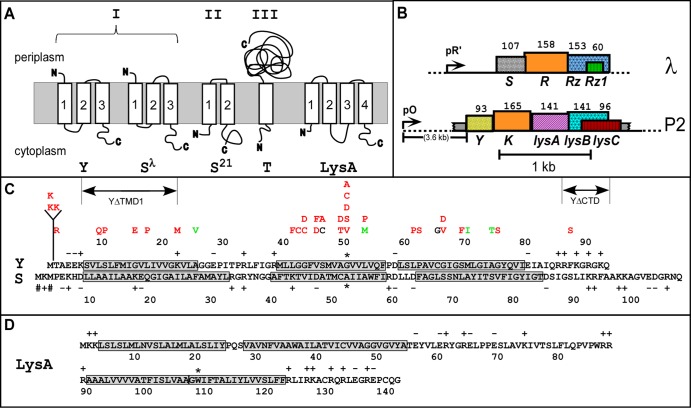
Fig 1.
Genes, sequences, and topologies. (A) Membrane topologies of P2 Y, λ S105, phage 21 S21, T4 T, and P2 LysA (see panel D). Three topology classes of the holins are indicated by Roman numerals. (B) The lysis cassettes of λ and P2. λ genes S, R, Rz, and Rz1 are shown along with late promoter pR′. P2 genes Y, K, lysA, lysB and lysC are shown along with late promoter pO. Genes are color coded according to their primary structure homology. Hatching pattern corresponds to homologous function. (C) Primary structures of Y (top) and S (bottom). Insertion, deletion, and missense changes relevant to the text are shown. Mutations are indicated above the Y sequence, color coded to phenotype: red = nonlytic; green = early lysis; black = normal lysis timing. Dual-start residues for S107 and S105 are indicated by # signs and the extent of the ΔTMD1 and ΔCTD deletions. Asterisks indicate the Ala52 residue in S105 and Gly52 in Y, chosen as analogous small residues in the central region of TMD2. (D) Primary structure and predicted topology of LysA. TMDs 1 and 2 were predicted by the algorithms TMHMM (27) and TMPRED (28). Both programs predicted a single TMD between 91 and 121. However, the homologous Y protein from a P2-like prophage in Enterobacter sp. 638 has a Lys residue at the position equivalent to Trp108 in Y, indicated by an asterisk, strongly suggesting that there are two TMDs in this hydrophobic stretch. This allows the highly basic N and C termini of LysA to be located in the cytoplasmic phase.