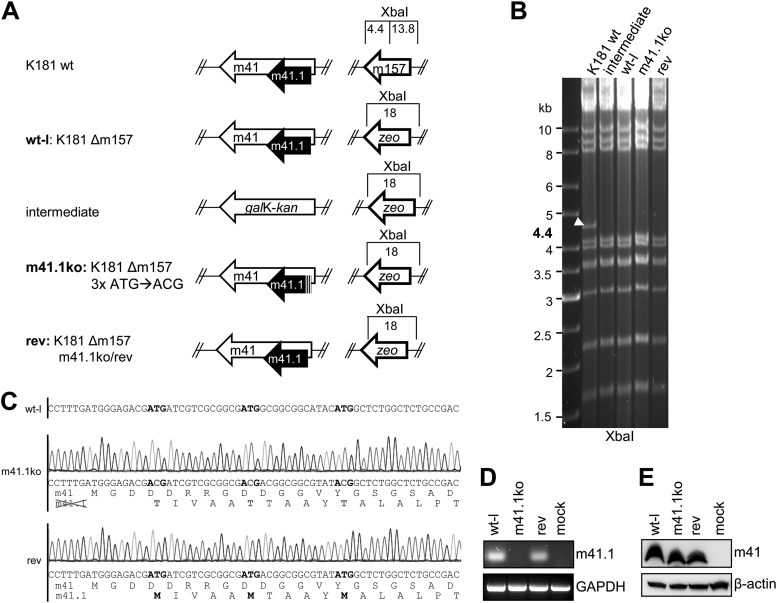
Fig 1.
Construction and genetic analysis of mutant MCMVs. (A) The m157 gene was replaced by a zeo marker within the MCMV K181 BAC to facilitate infection of C57BL/6 mice. This K181Δm157 virus was used as a wild-type-like (wt-l) virus in all experiments. To generate an m41.1ko virus, the m41 locus was first replaced by galK-kan followed by reinsertion of a mutated m41 ORF, in which the three ATGs of m41.1 had been changed to ACG. The revertant virus was constructed using the same two-step strategy. (B) BAC DNA of wt and mutant MCMV genomes was digested to check for m157 deletion with XbaI and separated on 0.6% agarose gels. A 4.4-kb fragment in the parental K181 BAC is indicated by an arrowhead. (C) Sequencing of wt-l, m41.1ko, and rev BAC DNA. In the wt-l sequence, ATG is highlighted in boldface. Point mutations within the m41.1 ATG codons are indicated in gray. Translated amino acid sequences are shown beneath the nucleotide sequences. (D) 10.1 fibroblasts were infected with wt-l, m41.1ko, and rev viruses. At 24 hpi, m41.1 expression was analyzed by RT-PCR using a forward primer that ends on the T of the second m41.1 ATG codon (5′-ATGATCGTCGCGGCGAT-3′ and 5′-GGAGGGCGCGACGAAAG-3′). GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (E) Expression of m41 was analyzed by immunoblotting in virus-infected RAW264.7 macrophages using the m41-specific antibody 2A6 (18).