Fig 2.
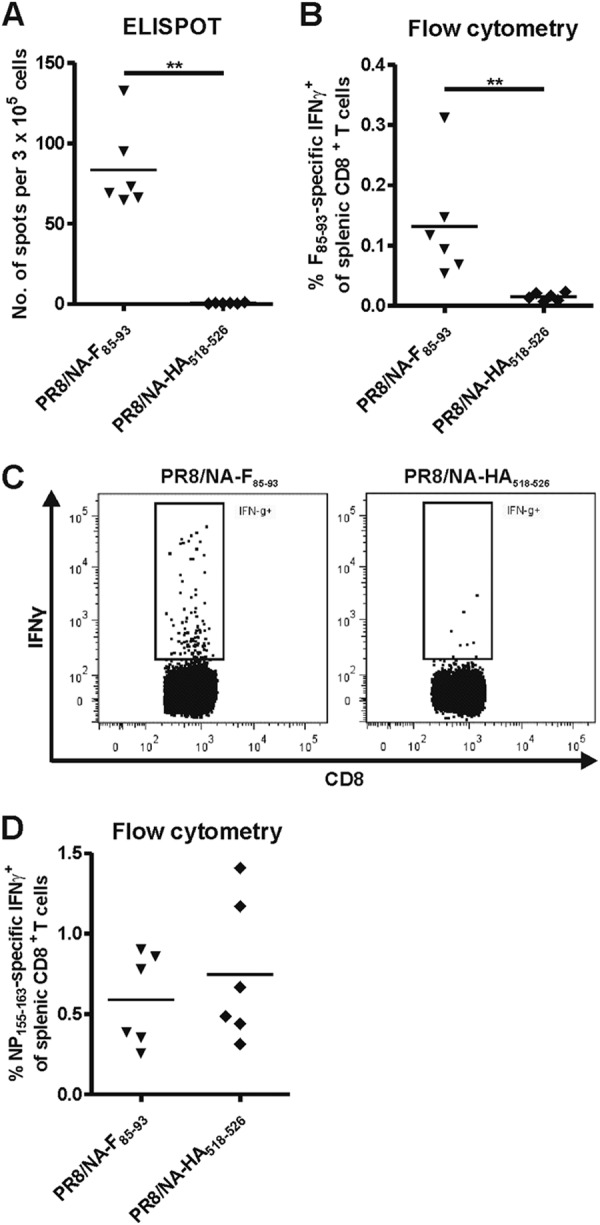
PR8/NA-F85–93 virus infection induces F85–93-specific CTLs in mice. BALB/c mice (6 per group) were infected with 5 × 103 PFU of PR8/NA-F85–93 or PR8/NA-HA518–526 virus. Spleens were isolated 10 days postinfection and stimulated with RSV F85–93 peptide (A, B, and C) or influenza virus NP155–163 peptide (D). After restimulation with RSV F85–93 peptide, IFN-γ production in splenic F85–93-specific CD8+ T cells was determined with ELISPOT assay (A) and flow cytometry (B). (C) Representative dot plots showing IFN-γ positivity in splenic CD8+ T cells after restimulation with RSV F85–93 peptide. (D) Splenocytes were restimulated with influenza virus NP155–163 peptide. The percentage of NP155–163-specific CD8+ T cells was determined by flow cytometry.
