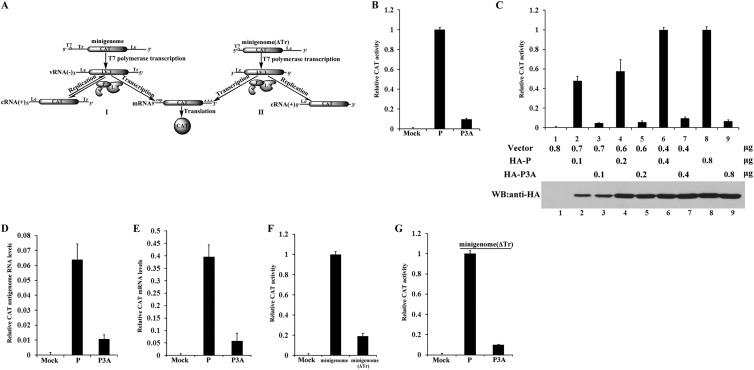
Fig 1.
N-terminal phosphorylation of P is essential for VSV minigenome transcription in vivo. (A) Schematic diagram of minigenome and replication-defective minigenome (ΔTr) systems. The negative-strand minigenome or ΔTr minigenome could be generated from transcription driven by T7 RNA polymerase in cells. Of the two, the former was encapsidated for transcription into the reporter gene mRNA, resulting in expression of CAT and its use as a template for replication by a complex of N, P, and L, but the latter was encapsidated and transcribed for reporter gene expression only. (B) BHK cells expressing T7 polymerase were transfected with plasmids encoding N, L, minigenome RNA, and P or P3A. Relative CAT expression levels in lysates were measured via CAT ELISA. The relative CAT expression level of cells transfected with a plasmid encoding P, as a positive control, was defined as 100%. (C) BHK cells expressing T7 polymerase were transfected with increasing quantities of plasmids encoding P or P3A together with the indicated plasmids in the minigenome system. Relative CAT expression levels were measured via CAT ELISA, and expression of P and P3A was detected via Western blot analysis (WB) with anti-HA antibody. (D and E) Transfection was performed as described for panel B. Relative CAT antigenomic RNA levels and mRNA levels were analyzed via RT-PCR, using β-actin as a reference gene. (F) BHK cells expressing T7 polymerase were transfected with plasmids encoding N, P, L, and the ΔTr minigenome, and relative CAT expression levels were measured as described for panel C. The CAT expression level of cells transfected with the minigenome, as a positive control, was defined as 100%. (G) The ΔTr minigenome is supported by P3A. The assay described for panel B was performed, but with the minigenome replaced with the ΔTr minigenome.