Fig 6.
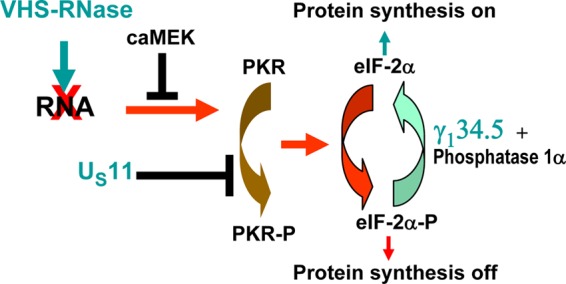
Schematic representations of the viral and cellular pathways that affect activation of protein kinase R (PKR). Early in infection the VHS RNase introduced into cells during the course of infection degrades the RNA that activates PKR. The VHS RNase is neutralized by the viral DNA synthesis-dependent onset of synthesis of VP16 (UL48) and VP22 (UL49). With the onset of synthesis of viral DNA, there is augmented synthesis of ICP34.5, the product of the γ134.5 gene; ICP34.5 recruits protein phosphatase 1α to dephosphorylate eIF-2α, there by enabling continuous protein synthesis in the infected cells. Late in infection, US11 may play a role in blocking PKR activation by binding to it. In addition, activated MEK blocks activation of PKR. PKR-P, phosphorylated PKR.
