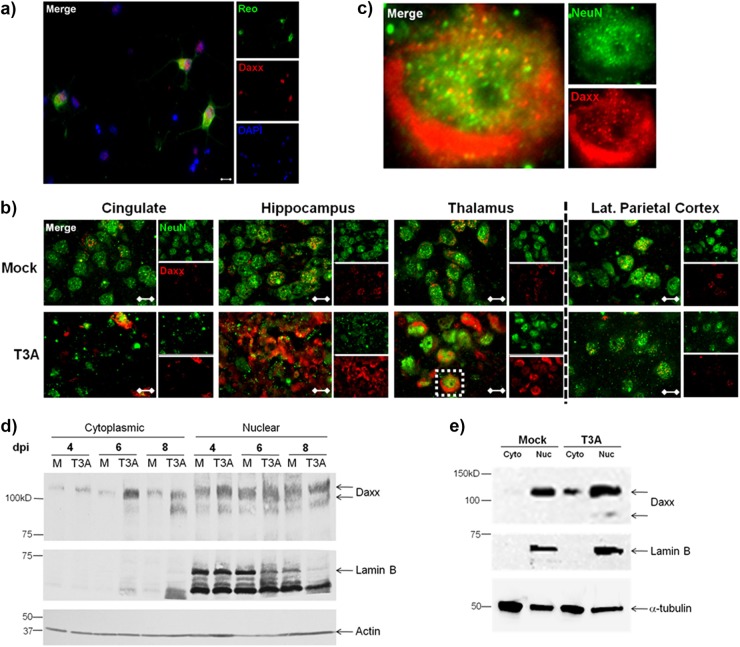
Fig 4.
Upregulated Daxx protein is localized to the cytoplasm of reovirus-infected neurons and L929 cells. (a) Primary hippocampal neurons were prepared from Swiss Webster mouse pups at the age of 0 to 1 day. Neurons were infected with T3A at 5 days in vitro and processed for immunocytochemistry at 7 dpi. Labeled Daxx (red) was found in neurons that were reovirus antigen σ3 positive (Reo; green). Magnification, ×400. Bar, 10 μm. (b) Two- to 3-day-old Swiss Webster mice were inoculated i.c. with 1,000 PFU T3A or an equal volume of PBS (mock). Brains were harvested at 4 to 8 dpi for immunohistochemical labeling of Daxx (red) and NeuN (green), a neuron-specific marker. Magnification, ×1,000. Bar, 10 μm. (c) An isolated cell in the thalamus (inset) is enlarged an additional 10× for demonstration of Daxx in NeuN-positive neurons. (d) Cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions prepared from brains extracted at 8 dpi from Swiss Webster mice that had been intracerebrally inoculated with 100 PFU T3A or an equal volume of PBS (mock). The cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were analyzed by Western blotting for detection of Daxx and lamin B nuclear marker. (e) L929 fibroblasts were treated with T3A reovirus at an MOI 20 or PBS (mock), and cells were harvested at 2 dpi for preparation of cytoplasmic (Cyto) and nuclear (Nuc) fractions. Western blotting was performed for detection of Daxx and the lamin B nuclear marker.