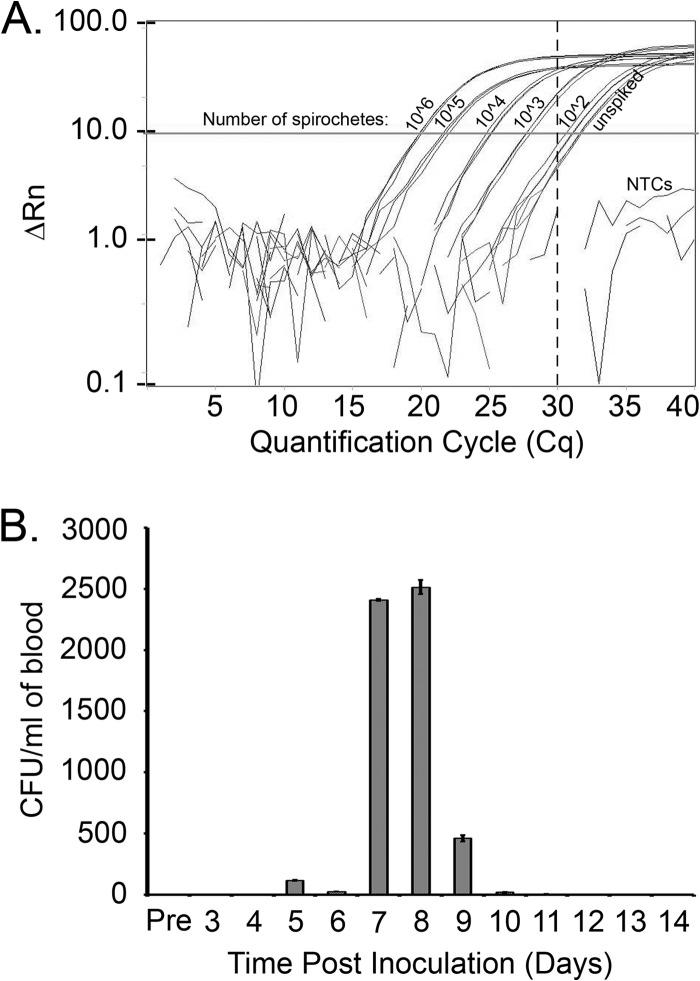
Fig 6.
iPCR has the potential to directly detect B. burgdorferi in infected samples. (A) Live spirochetes were serially diluted in HN buffer (106 to 102 spirochetes) and tested in triplicate using iPCR to detect organism capture using anti-B. burgdorferi antibody-coated magnetic beads. A call threshold was assigned at greater than or equal to five times the standard deviation (Cq = 30, vertical broken line) above the mean background signal, as determined using HN buffer alone (unspiked). PCR nontemplate controls (NTCs) included water and TBST used during the iPCR protocol. ΔRn, normalized change in fluorescence. (B) Six mice were prebled (Pre) and inoculated intradermally with 1 × 105 B. burgdorferi strain B31 A3 spirochetes. Approximately 50 μl of blood/mouse was collected every day from groups of two mice so that each group of two mice was bled every 3 days over a time period of 14 days. Blood collected from each mouse was plated in solid medium using 50 μl of blood and supplemented with a Borrelia antibiotic cocktail (see Materials and Methods for details), and the number of CFU per ml of blood was determined. Data shown are the average number of CFU/ml for the two mice sampled at each time point.