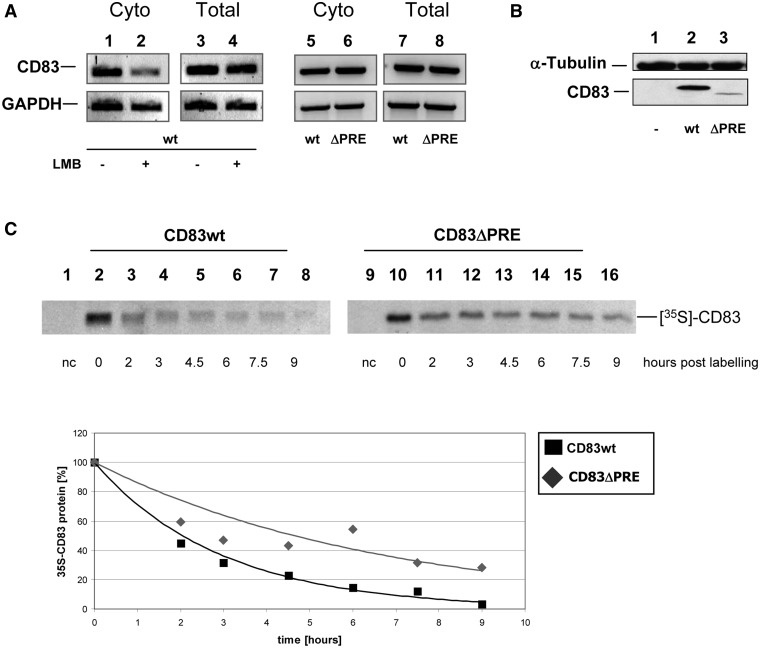
Figure 1.
CD83 mRNA with a PRE deletion is transcribed and translocated into the cytoplasm, but is translated inefficiently. (A) Full length CD83 (lanes 1–4, 5 and 7) or a CD83ΔPRE mutant construct (lanes 6 and 8) were transfected into COS7 cells. Ten nanomolars of leptomycin B was added to samples 2 and 4. Total (lanes 3, 4, 7, 8) and cytoplasmic RNA (lanes 1, 2, 5, 6) was harvested 48 h post-transfection and was analysed by RT-PCR. (B) COS7 cells transfected as described in (A) were harvested 48 h post-transfection, crude protein extracts were prepared and subjected to western blot analysis (lane 1: mock control, lane 2: CD83 wt, lane 3: CD83ΔPRE). (C) COS7 cells were transiently transfected with vectors expressing complete CD83 cDNA or a derivative thereof lacking the PRE sequence (CD83ΔPRE). Twenty-four hours post–transfection, de novo synthesized proteins were labelled with a 35S-translabel pulse (1 h). For chase, cell cultures were maintained in label-free medium for the indicated periods. Crude extracts were subjected to CD83 immunoprecipitation followed by sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE). Protein stabilities were quantified by phosphorimaging (lane 1/9: negative control; lane 2–8: CD83 wt; lane 10–16: CD83ΔPRE; lanes 2 and 10: newly synthesized CD83 protein variants; residual lanes: indicated time points post labelling). Lower panel: quantification of relative CD83 protein levels over time for CD83 wt (black square) or for CD83ΔPRE (grey rhombus).