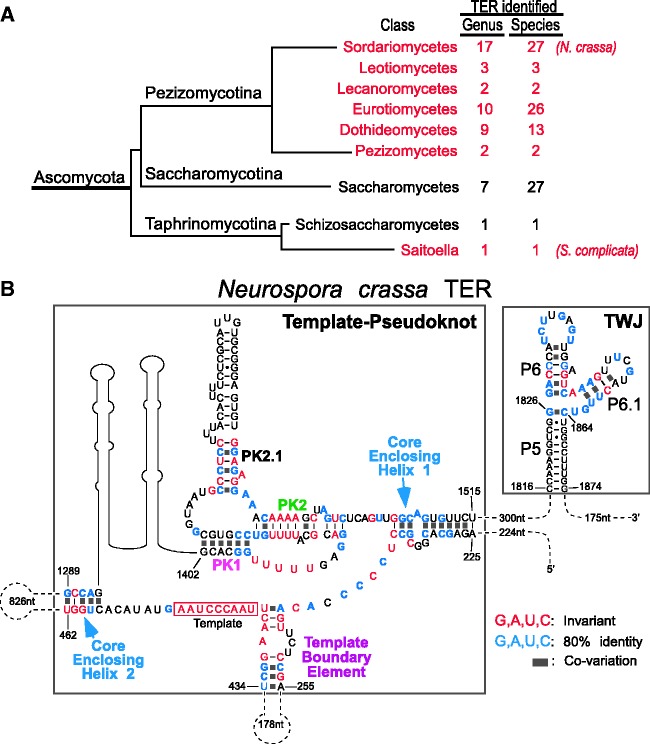
Figure 4.
Secondary structure model of the NcrTER core domains. (A) Number of fungal TER sequences identified. In this study, 73 new TER sequences were identified from six Pezizomycotina classes (red) and one Taphrinomycotina TER sequence from S. complicata. The number of TER sequences identified in each class is indicated. Branch length is not proportional to evolutionary distance. (B) Secondary structure model of the NcrTER core domains: the template–pseudoknot and the TWJ that includes the P5, P6 and P6.1 stems. Invariant nucleotides (red) or nucleotides with ≥80% identity (blue) as well as base pairings supported by co-variations (solid gray boxes) are indicated. Other major structural features shown include the core-enclosing helices 1 and 2, template boundary element, template and the pseudoknot helices PK1, PK2 and PK2.1. The regions without secondary structure determined are indicated by dotted lines, with the number of omitted residues indicated.