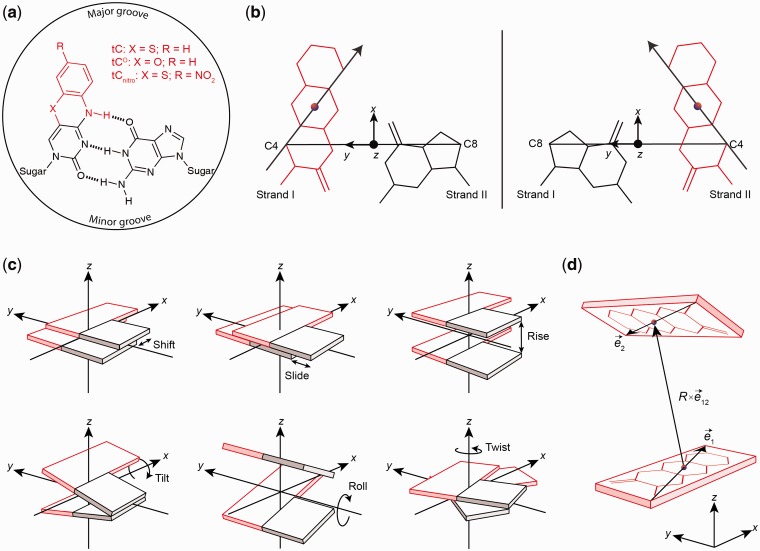
Figure 1.
Using base probe building blocks for constructing 3D nucleic acid models and base–base FRET simulations. (a) Chemical structures of the tC base probes in their base pairing environment with guanine. tC and tCO may act as FRET donor with tCnitro as acceptor. (b) Definition of local tC–G base pair coordinate frame with tC in strand I (left) and strand II (right). In the base pair coordinate frame the y-axis is parallel to the line connecting the C4 atom of the tC base and the C8 atom of the complementary G base pointing from strand II to strand I. The z-axis points in the 5′→3′ direction of strand I, and the x-axis completes a right-handed set. The origin of the base pair frame is the midpoint of the C4–C8 line. (c) Definition of base pair step parameters used to construct 3D nucleic acid geometries. Shift, slide and rise are translational parameters, whereas tilt, roll and twist are rotational parameters. (d) Definition of 3D unit vectors used to simulate FRET in the constructed nucleic acid geometries.