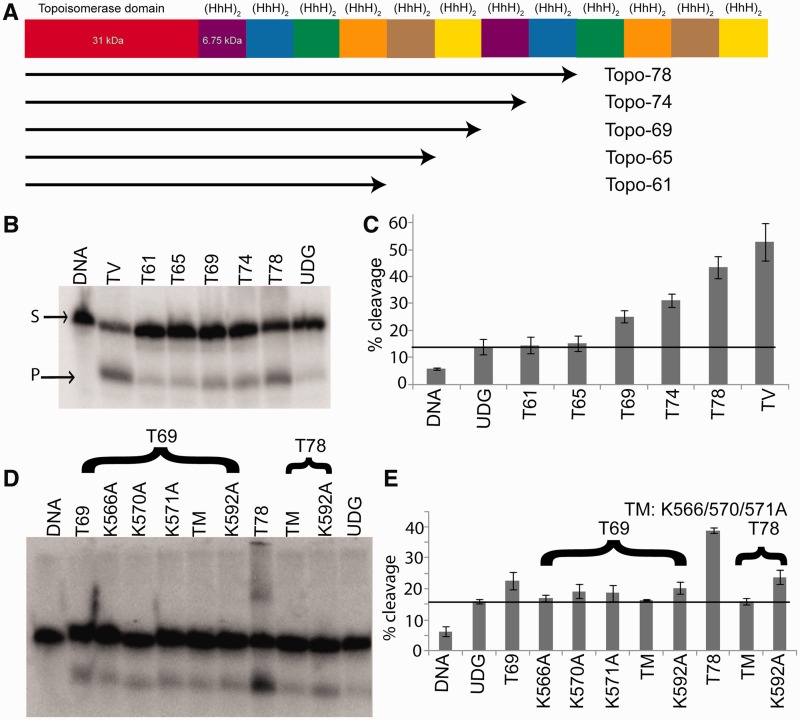
Figure 1.
AP lyase activity of the different Topo-V fragments. (A) Schematic representation of the Topo-V protein and the various fragments used in the present study. (B) AP lyase assay with different Topo-V fragments. The upper band corresponds to uncleaved DNA (S), whereas the lower band on the gel shows the product after cleavage of the DNA at the abasic site (P). (C) Graph showing quantification of the AP lyase activity for different Topo-V fragments (three replications). The partial cleavage of the DNA and UDG controls is due to the inherent instability of abasic DNA. Topo-69 is the shortest Topo-V fragment with AP lyase activity and indicates that the active site lies between residues 556 and 599. (D) Identification of the nucleophilic Lys involved in AP lyase activity of Topo-78. All the Lys residues in the region spanning 556–599 were mutated to Ala. (E) Graph showing AP lyase activity of different Lys mutants (three replications). The results from Topo-78 fragments show that mutating K566, K570 and K571 have an effect on AP lyase activity, whereas the K592 mutant does not show an effect. Error bars represent the standard deviation for three replications. The black line in (C) and (E) represents the basal activity due to the instability of DNA substrate. TM refers to the K566A, K570A, K571A triple mutant.