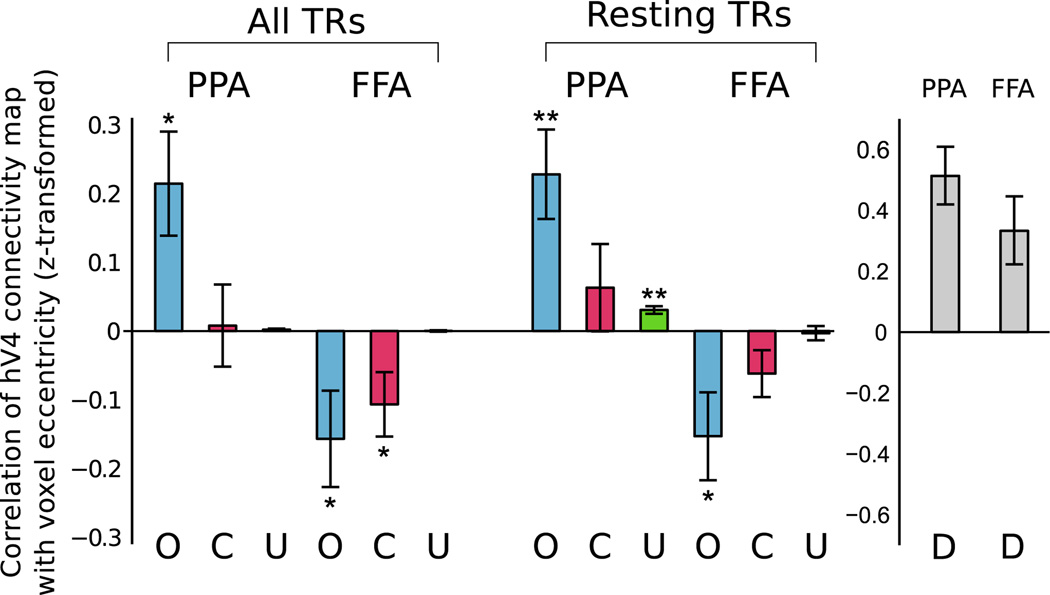
Fig. 6.
hV4 eccentricity differences for optimal values of λ. After choosing an optimal λ value for each subject bfased on generalization performance (see Fig. 5), we compute the eccentricity of hV4 connectivity maps for seed regions PPA and FFA, using our method (O), a voxel correlation method (C), and our method without regularization (U) (results averaged across four runs for each subject). Whether using all timepoints from a run (306 TRs) or using only those timepoints during which no stimulus was presented (approx. 148 TRs), our method finds that connectivity with PPA increases with increasing eccentricity, while the opposite is true for FFA. The correlation and unregularized controls are much less sensitive, showing significantly smaller differences between PPA and FFA eccentricity biases. Additionally, our results cannot be explained simply by local noise correlations; since both PPA and FFA are closer to the anterior (peripheral) side of hV4, such a model would predict similar peripheral eccentricity biases in PPA and FFA (D). Error bars indicate standard error, *p<0.05, **p<0.01.