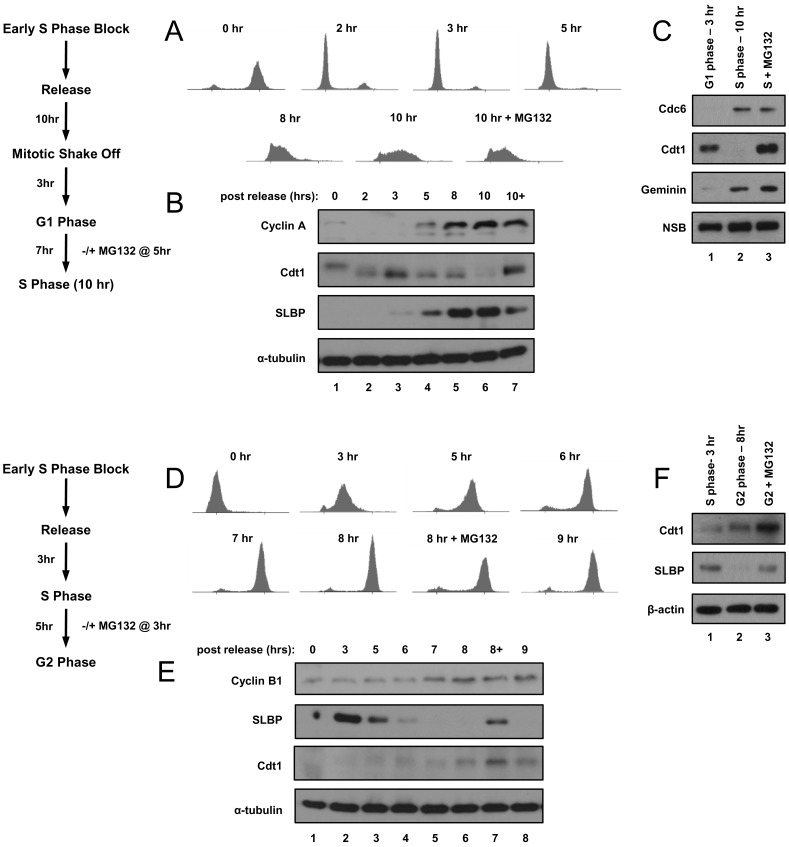
Figure 1. HeLa cell synchronization.
A) Cells were synchronized by a modified double-thymidine block then released by re-plating and harvested at the indicated time points; a late G1 phase culture was treated with MG132 two hrs prior to harvest in early S phase. Synchrony was determined by flow cytometric analysis of DNA content. B) Immunoblot analysis of endogenous Cyclin A, Cdt1, SLBP, and tubulin proteins in whole cell lysates from portions of the same cells used in A. C) Cells were metabolically labeled with stable isotopes and then synchronized in G1 (3 hrs after mitosis, normal/“light” isotopes) and early-S phase (10 hrs after mitosis, labeled with intermediate or “medium” isotopes) as in A and B. Cells labeled with the heaviest isotopes were treated with MG132 two hrs prior to harvest in early S phase. Immunoblot analysis of endogenous Cdc6, Cdt1, and geminin in whole cell lysates used for subsequent mass spectrometric tests. A non-specific band (NSB) serves as a loading control. D) Cells were synchronized by double-thymidine block, released into S phase, and harvested at the indicated timepoints. Synchrony was determined by flow cytometric analysis of DNA content. E) Immunoblot analysis of endogenous Cyclin B, SLBP and Cdt1 in whole cell lysates from portions of the same cells used in D. F) Cells were metabolically labeled with stable isotopes and synchronized in S phase (light isotopes) or G2 phase (medium isotopes) as in D and E. A culture labeled with heavy isotopes was treated with MG132 in late S phase for two hrs prior to harvest in G2. Immunoblot analysis of endogenous Cdt1 and SLBP in whole cell lysates used for subsequent mass spectrometric analysis; β-actin serves as a loading control.