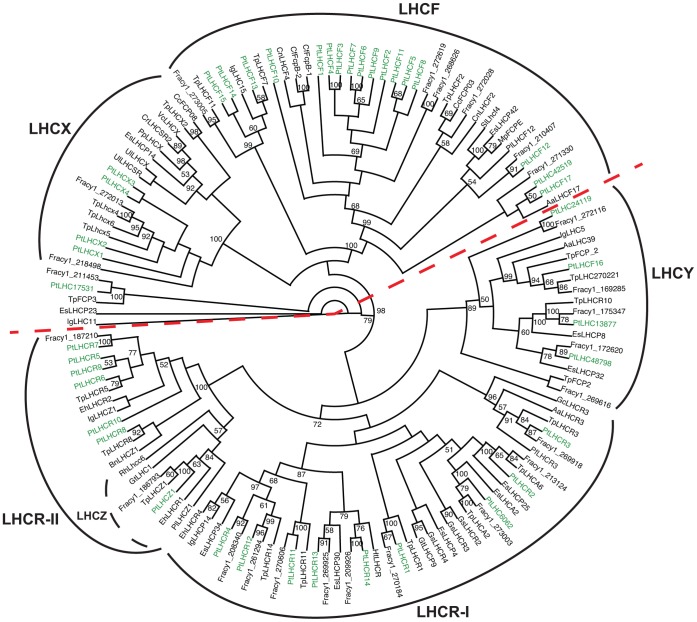
Figure 4. Cladogram of the antenna proteins of P. tricornutum.
Phylogenetic analysis of all predicted P. tricornutum antenna proteins belonging to the light-harvesting complex (LHC) superfamily, together with other Stramenopile LHC proteins sequences as well as sequences from cryptophytes, haptophytes, rhodophytes, viridiplantae, rhizaria and an alveolate. LHCs from P. tricornutum are indicated in green. The two main clades are separated by a dashed red line. The abbreviations used are Aa: Aureococcus anophagefferens; Bn: Bigelowiella natans; Cc: Cyclotella cryptica; Cf: Cylindrotheca fusiformis; Cn: Chaetoceros neogracile; Cr: Chl amydomonas reinhardtii; Eh: Emiliania huxleyi; Es: Ectocarpus siliculosus; Fracy1: Fragilariopsis cylindrus; Gc: Gracilaria changii; Gs: Galdieria sulphuraria; Gt: Guillardia theta; Ht: Heterocapsa triquetra; Ig: Isochrysis galbana; Mp: Macrocystis pyrifera; Sl: Saccharina latissima; Pf: Pseudochattonella farcimen; Pl: Pavlova lutheri; Pp: Physcomitrella patens subsp. Patens; Pt: Phaeodactylum tricornutum; Rh: Rhodomonas sp. CS24; Tp: Thalassiosira pseudonana; Ul = Ulva linza; Vc: Volvox carteri f. nagariensis. The accession numbers corresponding to the protein sequences used in the analysis are listed in Table S3.