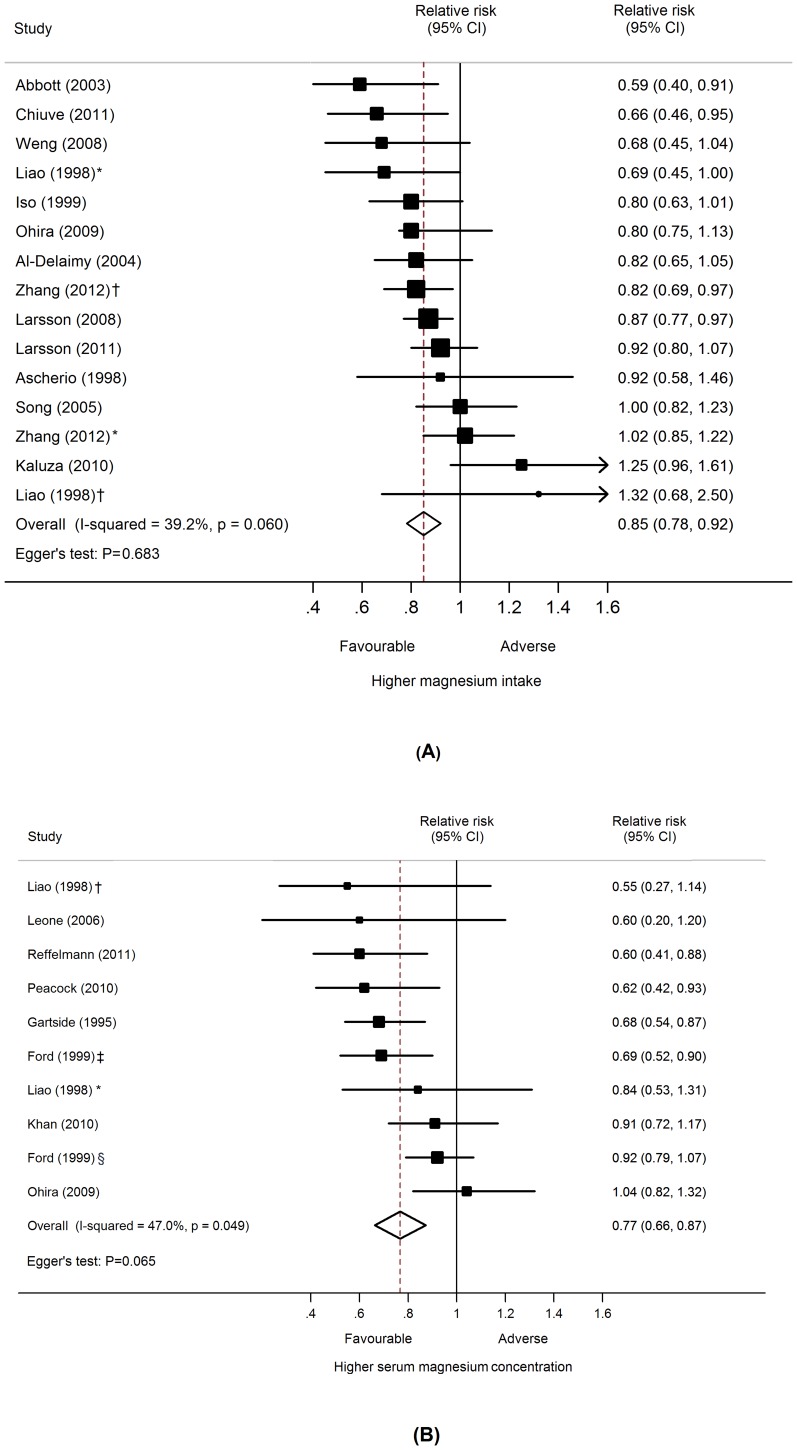
Figure 1. Dietary magnesium intake, serum magnesium concentrations, and the risk of total CVD events.
(A) Dietary magnesium intake; (B) Serum magnesium concentrations. Adjusted relative risks for the association between dietary magnesium intake and serum magnesium concentrations (highest vs. lowest categories) and the risk of total CVD events were sorted by statistical size, defined by the inverse of the variance of the relative risks. CI = confidence interval; RR = relative risk. *Male participants. †Female participants. ‡CVD death outcomes. §CHD outcomes.