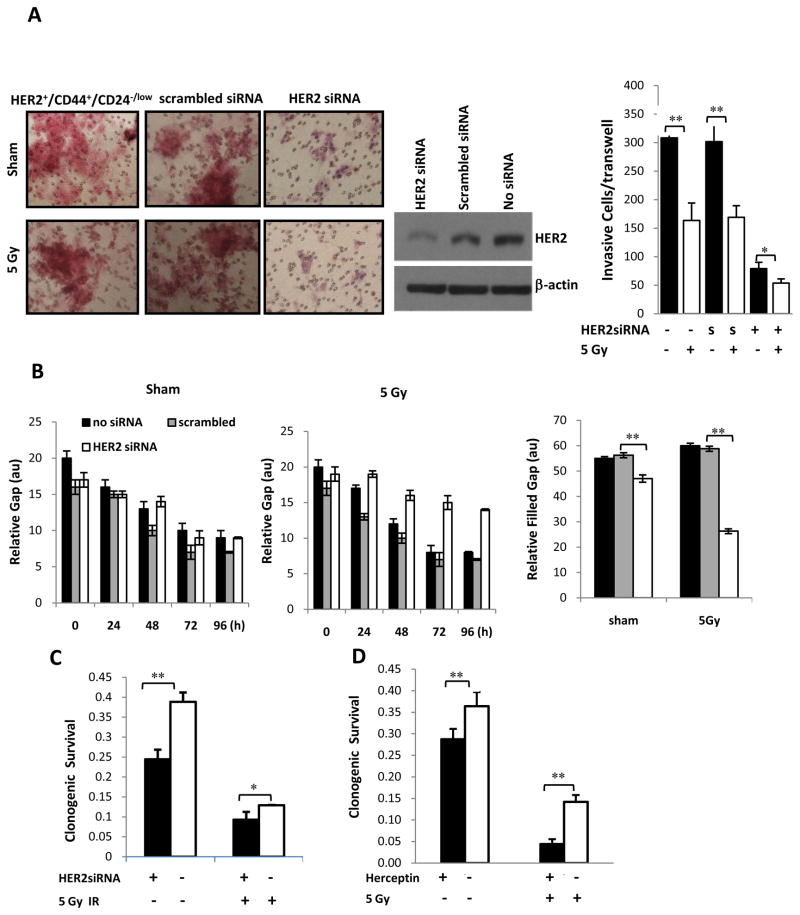
Figure 4.
Inhibition of HER2 blocks the aggressiveness and radioresistant phenotypes of HER2+/CD44+/CD24−/low BCSCs. (A) Left panel represents depicted images of Matrigel invasion assays of HER2+/CD44+/CD24−/low BCSCs at 72 h after 5 Gy IR and treatment with scrambled or specific HER2 siRNA. Middle panel, depicts the specific capacity of HER2 siRNA to reduce HER2 expression in HER2+ breast cancer stem cells. Right panel represents quantification of the number of cells invading the membrane per transwell. Data represents mean+SE of n = 6 and statistical analysis was performed with *p<0.05, **p<0.01). (B) Represents the gap filling values determined at different time points post cell’s injury (0 to 96 h) in sham (0 Gy) and irradiated cells (5Gy) and in cells treated with specific or scrambled siRNA against HER2. Right panel represent mean +SE of the gap filling rate calculated from n = 6 independent experiments; **p<0.01). (C, D) The effect of targeting HER2 signaling pathway on aggressiveness and radiosensitivity of BCSCs. HER2+/CD44+/CD24−/low were treated either with siRNA (C; n = 3; *p<0.05; **p<0.01) or with anti- HER2 antibody, Herceptin, (D; 10 μg/ml for 5 days, n = 3; **p<0.01). The clonogenic sensitivity to IR was evaluated following sham or 5 Gy IR (mean+SE; n=3).