Figure 2.
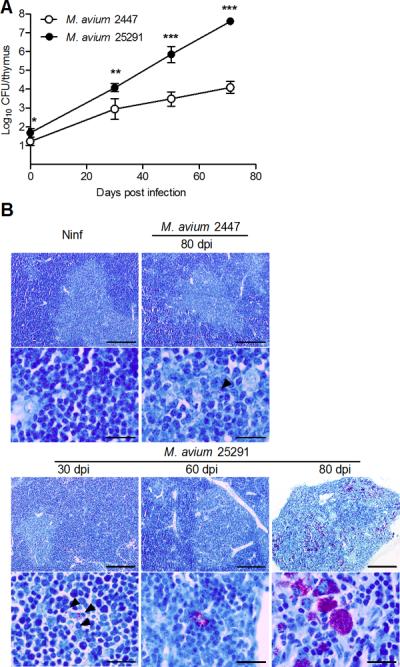
Infection with M. avium strain 25291 leads to higher bacterial loads in the thymus as compared with strain 2447.
A. Representative kinetics of M. avium infection of the thymus from WT mice inoculated with strains 2447 or 25291. Data represent the mean and standard deviation of CFU from five mice per group from one out of three experiments. Statistically significant differences between mice infected with strains 2447 and 25291 are labeled as *p<0.05, **p<0.01, *** p<0.001. B. Representative thymic sections from non-infected mice (Ninf) and mice infected with strains 2447 or 25291 stained for acid-fast bacteria (Ziehl-Neelsen method). Scale bars represent 200 μm in the low-power views and 20 μm in the high magnification pictures. Arrowheads indicate acid fast bacteria in cases of low infection burden.
