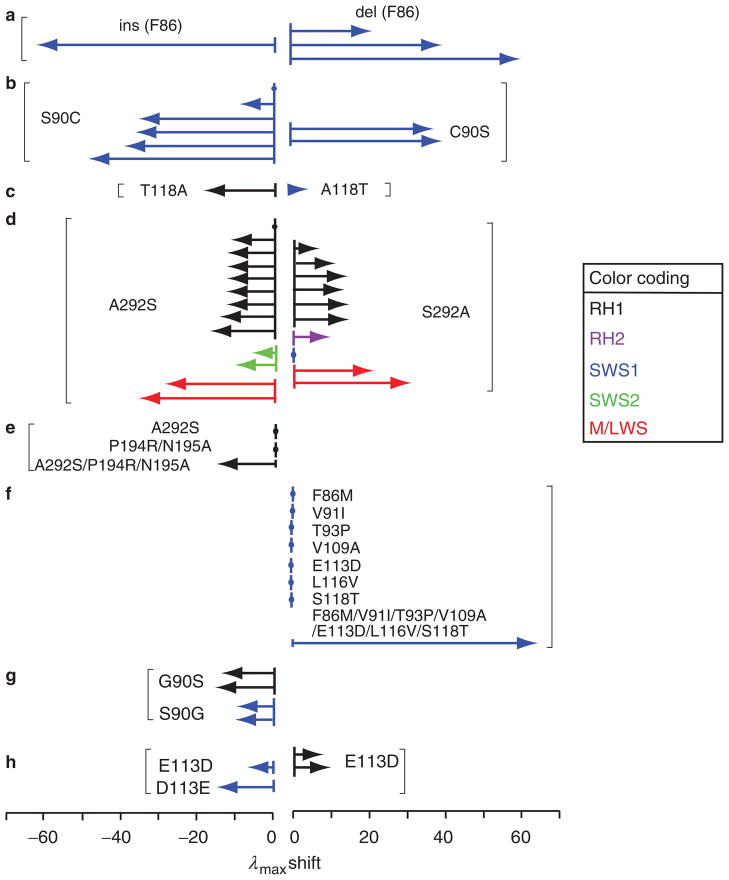
Figure 2.
Examples of shifts in the wavelength of maximum absorption (λmax, in nanometers) affected by amino acid interactions. The black, purple, blue, green, and red colors indicate various RH1, RH2, SWS1, SWS2, MWS, and LWS pigments. The arrows reflect the λmax shifts of visual pigments from different species and are named in order from top to bottom within each example. (a) The insertion (ins) of F86 in the SWS1 pigment of scabbardfish (Lepidopus fitchi) and deletions (del) of F86 in the SWS1 pigments of a vertebrate ancestor, the lampfish (Stenobrachius leucopsarus) and the bluefin killifish (Lucania goodei) (Tada et al. 2009). (b) S90C in the SWS1 pigments of the mouse (Mus musculus), the cow (Bos taurus), an avian ancestor, the pigeon (Columba livia), the frog (Xenopus laevis), and the chicken (Gallus gallus) and C90S in the SWS1 pigments of the budgerigar (Melopsittacus undulatus) and the zebra finch (Taeniopygia guttata). (c) T118A in the RH1 pigment of the cow and A118T in the SWS1 pigment of the budgerigar. (d) A292S in three ancestral, five bovine, and one tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) RH1 pigments; in the SWS2 pigments of the bluefin killifish and the newt (Cynops pyrrhogaster); and in the LWS pigments of two ancestral M/LWS pigments and S292A in the RH1 pigments of the scabbardfish, the coelacanth (Latimeria chalumnae), the cichlid, the thornyhead (Sebastolobus altivelis), the viperfish (Chauliodus macouni), and the conger (Conger myriaster); in the RH2 pigment of the medaka (Oryzias latipes); in the SWS1 pigment of the human (Homo sapiens); and in the M/LWS pigments of the mouse and the dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) (Yokoyama 2008, Yokoyama et al. 2008a). (e) Single and multiple mutations in the RH1 pigment of the conger. (f) Single and multiple mutations in the SWS1 pigment of a frog ancestor (Takahashi and Yokoyama 2005). (g) G90S in two bovine RH1 pigments and S90G in bovine and human SWS1 pigments. (h) E113D in the SWS1 pigments of the frog and of its ancestor and E113D in two bovine RH1 pigments. See Yokoyama (2008) and the references therein.