Figure 1.
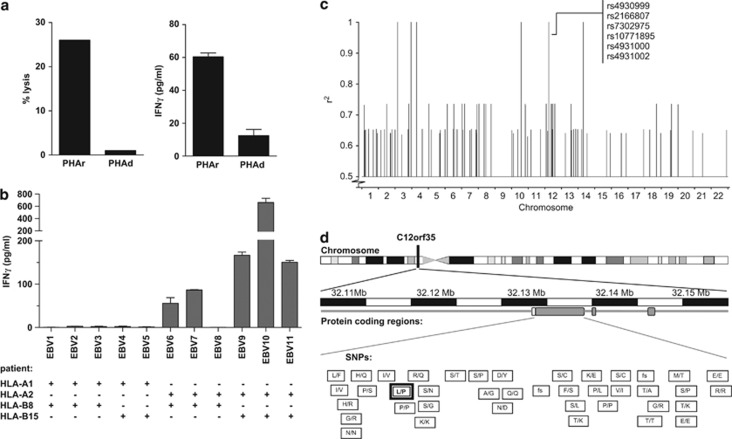
T-cell clone 503A1 selectively recognizes an HLA-A*02-restricted mHag, which is encoded by a non-synonymous coding SNP on chromosome 12. (a) Cytotoxic T-cell clone 503A1 lyses antigen-presenting cells (APC) from the SCT recipient but not from the donor in a conventional chromium release assay (left graph). PHA-blasts of both recipient and donor are used as APC. Clone 503A1 also produces a greater amount of IFN-γ when in contact with recipient APC in comparison to donor APC (right graph).(b) In a panel of EBV-LCLs only those cells that are at least HLA-A*02 positive are recognized by CTL 503A1. Five out of six random selected HLA-A*02 positive EBV-LCL test positive in this IFN-γ ELISA experiment. (c) Genome-wide zygosity-genotype correlation analysis using the zygosities of 30 CEPH-individuals led to 15 100% correlating SNPs located on chromosomes 3, 4, 10, 12 and 14. After correlating them with the mHag+ CEPH-individuals with undeducible zygosities, six SNPs on chromosome 12 were still in 100% correlation with the experimental data. Of these, only SNP rs2166807 leads to the transcription of a peptide. (d) SNP rs2166807 (bold box) is located on gene C12orf35 on chromosome 12, together with several other SNPs. The letters in the boxes represent the alterations in amino acids caused by the polymorphisms in this region. Also, frameshift (fs) SNPs are depicted.