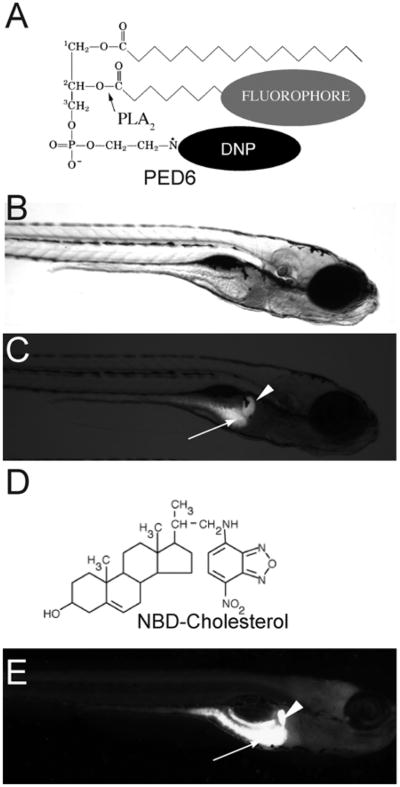
Fig. 8.
PED6 and NBD-cholesterol visualize lipid uptake in larval zebrafish. (A) The chemical structures of PED6. The BODIPY-labeled acyl chain of PED6 is normally quenched by the dinitrophenyl group at the sn-3 position. Upon PLA2 cleavage at the sn-2 position, the BODIPY-labeled acyl chain is unquenched and can fluoresce. Bright field (B) and fluorescent (C) images of 5 dpf larva following soaking in PED6 for 6 h. PED6 labeling reveals lipid processing in the gall bladder (arrowhead) and intestine (arrow). (D) The chemical structure of NBD-cholesterol. The NBD-cholesterol analog contains a NDB fluorophore where the alkyl tail at the terminal end of cholesterol would normally reside. (E) Soaking zebrafish larvae (5 dpf) in NBD-cholesterol (3 mg/ml, solubilized with fish bile) for 2 h visualizes cholesterol uptake in the gall bladder (arrowhead) and intestine (arrow).