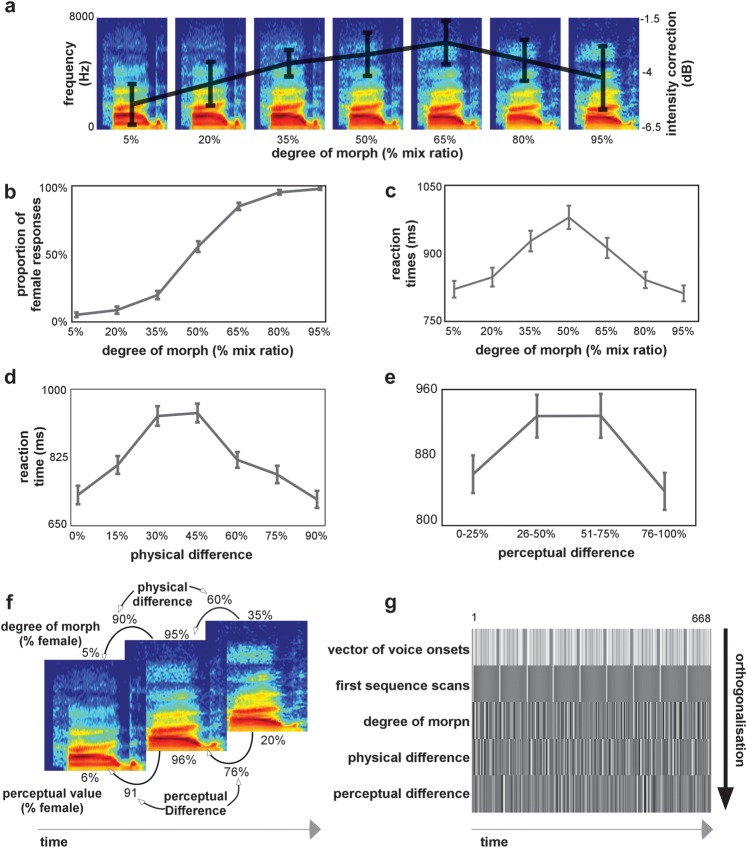
Figure 1.
(a) Stimuli were voices derived from male-to-female voice gender continua. Example of a continuum where the physical interpolation was done with mix ratios increasing by 15%. Superimposed on the continua is the average intensity level correction for each degree of morph derived from the pilot study on perceived loudness. The error bars show the standard error computed from the average variation in intensity correction between the 9 different continua. (b) Voice gender psychophysical function: the group-average proportion of female responses is shown as a function of the degree of morph. For panels b–e, the error bars show the standard error computed from the individual subject's classifications. (c) Reaction times: the group-average reaction times as a function of the voices' degree of morph. (d) Reaction times: the group average reaction times as a function of the physical difference with the previously heard stimulus. (e) Reaction times: the group average reaction times as a function of the perceptual difference with the previously heard stimulus. (f) Illustration example for the definition of the parametric regressors: Spectrogram examples of 3 consecutive voices in the stimulation sequence. Shown above the spectrogram is the voice's respective degree of morph value and the physical difference with the previous stimulus. Shown below the spectrogram is the voice's perceptual value (for a given subject) and the perceptual difference with the previous stimulus. (g) Design matrix: the first row of the design matrix defines the stimulus onsets for the 9 continua (each continuum separated by baseline trials). The following rows represent the parametric regressors included in the general linear model. The first regressor models the first stimulation in a sequence. Since this stimulus is not preceded by another voice, we model it out of the regression. The second regressor models the voice's degree of morph. The third regressor models the physical difference between consecutive voices, and finally, the fourth regressor models the perceptual difference between consecutive voices.