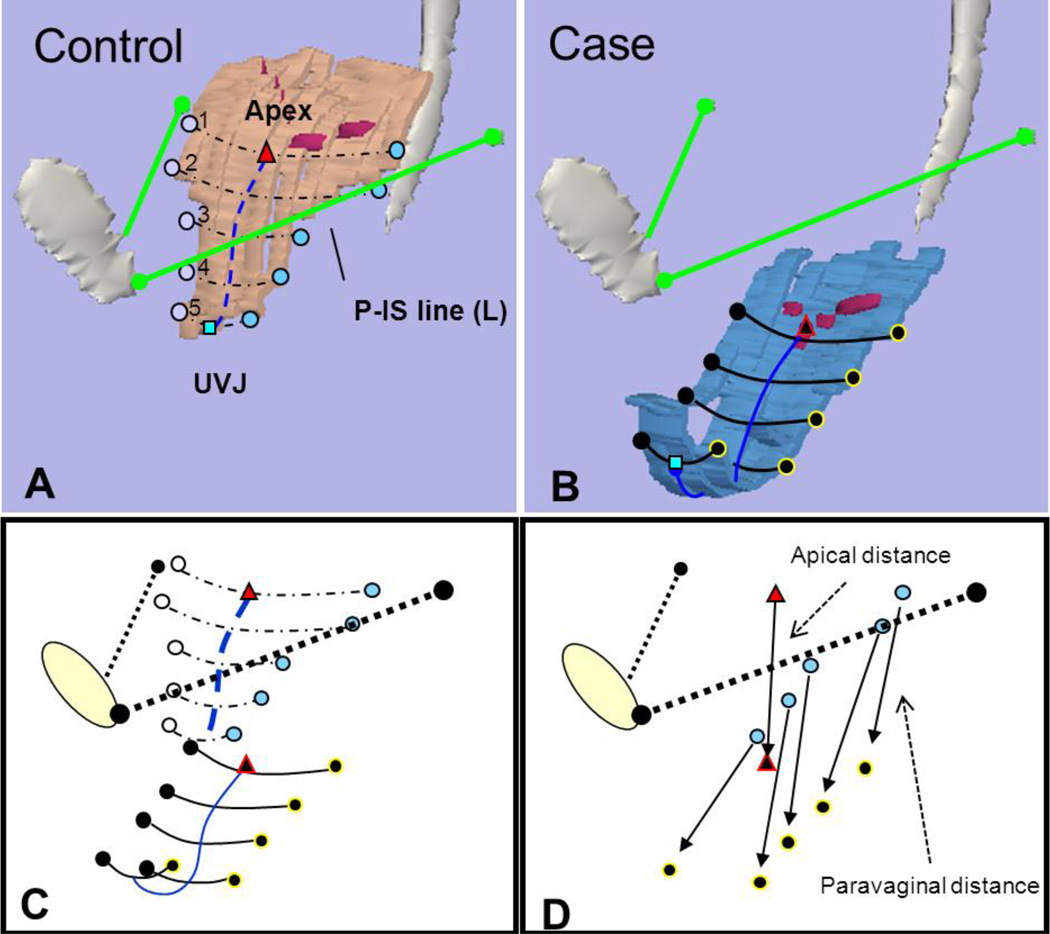
Fig 3. Determining distance from normal.
(A) Vaginal width and lateral wall locations at 5 equidistant points from apex at cervicovaginal junction to urethrovaginal junction (UVJ) in normal support. Pubis-ischial spine (P-IS line) in green from insertion of ATFP on pubic symphysis to ipsilateral ischial spine. (B) Similar markings in anterior compartment prolapse. Note, cervicovaginal junction modeled as purple dots along vaginal wall. (C) Alignment of control and prolapse data using P-IS reference line. (D) The distance that lateral locations and apex lie from normal is shown with arrows extending from normal location to location in prolapse. Triangle – apex, square – UVJ, circles – lateral vaginal wall, blue lines – vaginal length. © DeLancey 2010