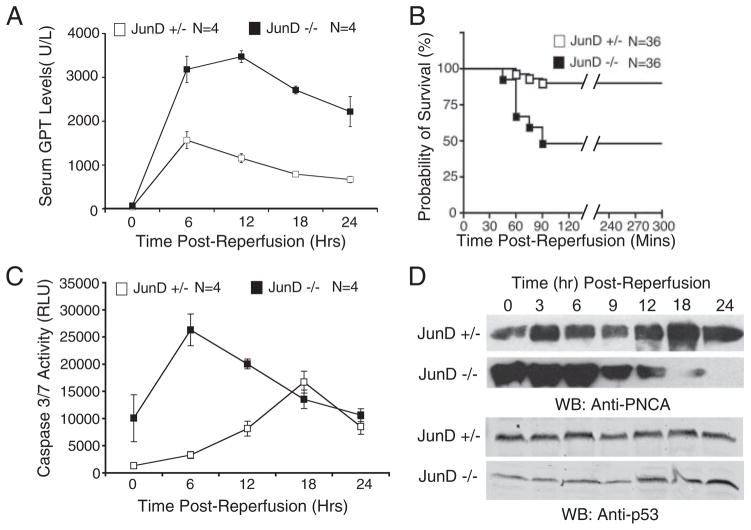
FIGURE 2. JunD protects against I/R-induced liver injury and alters hepatocellular remodeling.
JunD−/− and JunD+/− mice were subjected to I/R injury, with partial lobar hepatic ischemia taking place for 45 min (A, C, and D) or 60 min (B), followed by the indicated times of reperfusion. A, serum samples were collected by cardiac puncture at the indicated time points following the start of reperfusion and assayed for GPT. Results depict the mean (±S.E.) units/liter of GPT for n = 4 animals in each group. B, survival of mice following 60 min of ischemia was plotted using a Kaplan-Meier survival curve, p < 0.0004. C, caspase 3/7 activity in whole cell lysates from liver was determined using a caspase-Glo detection kit, for which a substrate emits light when cleaved by either caspase 3 or 7. Results depict the mean (±S.E.) relative light units (RLU). D, for each experimental point, pooled liver lysates from three animals were evaluated for PCNA and p53 expression by Western blotting (WB). The 0-h time point in A, C, and D represents the respective values (serum glutathione S-transferase, caspase 3/7 activity, or PCNA/p53 levels) for non-I/R injured control animals (i.e. noninjured base-line values).