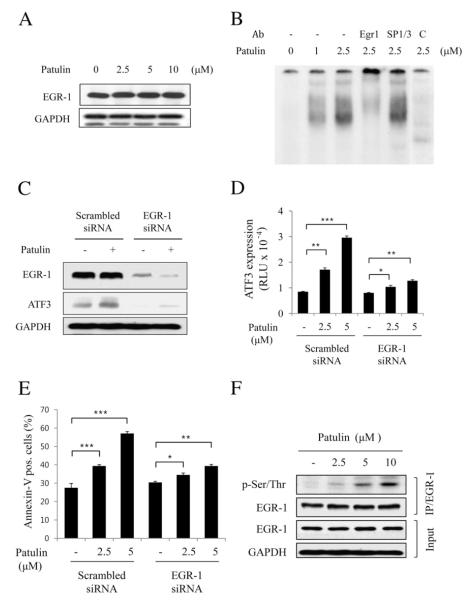
Fig. 4.
EGR-1 is required for patulin-induced ATF3 expression in HCT116 cells. (A) Cells were treated with various concentrations of patulin for 24 h, and then lysed for measurement of EGR-1 by western blot analysis. (B) EMSA analysis. Nuclear fraction (10 g) obtained from the cells treated with patulin at the indicated concentrations was applied to EMSA analysis using GC-rich oligonucleotide as described in Materials and methods. For supershift, EGR-1 or SP1/SP3 antibody (1 μg) was added into the EMSA reaction mixture. As a competitor, unlabeled cold oligonucleotide was added into the reaction mixture (lane 6). (C) EGR-1 knockdown abrogates patulin-induced ATF3 expression. Cells were transfected with EGR-1 siRNA or scrambled siRNA for 48 h followed by patulin treatment at 5 μM for 24 h. Proteins were detected by western blotting. (D) Effect of EGR-1 knockdown on patulin-induced ATF3 promoter activity. After transfection with EGR-1 siRNA or scrambled siRNA for 24 h, cells were transiently transfected 2 μg pATF3-luc plasmid prior to patulin treatment for further 24 h. Luciferase activity was measured and expressed as means±SE from a representative triplicate experiment performed three times independently. Statistical significance was determined by Dunnett’s test (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001) followed by one-way ANOVA. (E) FACS analysis for the determination of the effect of EGR-1 knockdown on patulin-induced cell apoptosis. All the procedures were similar to Fig. 2C. Data are expressed as means±SE from a representative triplicate experiment. Statistical significance was determined by Dunnett’s test ((*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001) followed by one-way ANOVA. (F) Effect of patulin on EGR-1 phosphorylation. Cells were treated with varying concentrations of patulin for 24 h, and then lysed for immunoprecipitation with anti-EGR-1 antibody. The immunoprecipitates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-p-Ser/Thr antibody. The membrane was then stripped and reprobed with anti-EGR-1 antibody.