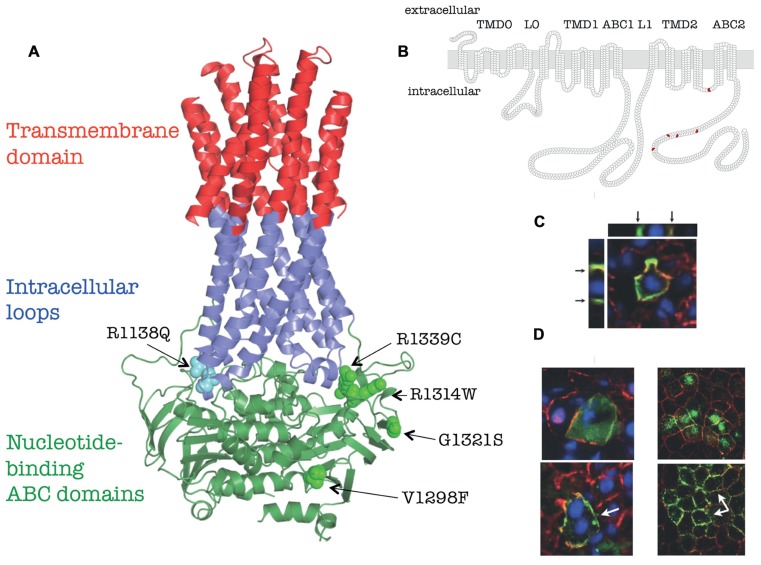
FIGURE 1.
Membrane topology, homology model and in vivo localization of human ABCC6 and its mutants (based on Le Saux et al., 2011). (A) Homology model of human ABCC6. The position of the missense mutants studied are indicated. (B) Membrane homology model of human ABCC6. The domain structure are indicated on the top, the position of missense mutants are shown in red. (C) Colocalization of the endogenous mouse Abcc6 (red) and human ABCC6 (green) in vivo in mouse liver after HTVI-delivery of ABCC6 cDNA by confocal microscopy. Arrows indicate the basolateral localization on Z-stack cross/sections. (D) Effect of 4-PBA on membrane targeting of Q1314W. Left panel: colocalization of the endogenous mouse Abcc6 (red) and human ABCC6 mutant (green) in vivo in mouse liver after HTVI-delivery of ABCC6 cDNA without 4-PBA treatment (upper panel) or with 4-PBA treatment (lower panel). Right panel: colocalization of the endogenous dog Na/K-ATPase (red) and human ABCC6 mutant Q1314W (green) in vitro in polarized MDCKII cells without 4-PBA treatment (upper panel) or with 4-PBA treatment (lower panel). White arrows point to the altered membrane localization.