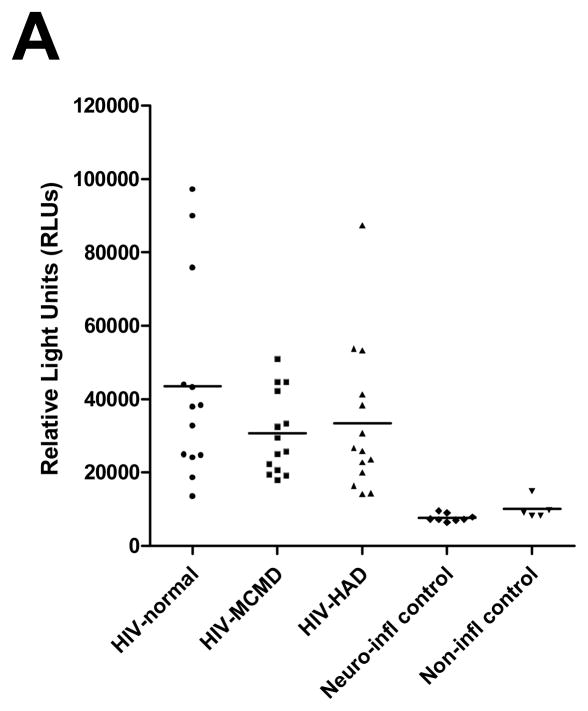
Fig 1.
Relative Light Units of an ELISA for anti-Tat antibodies detected in spinal fluid of HIV-infected individuals without dementia (HIV-Normal) (MSK 0) (n=15; 86.7% > mean+1SD), with mild cognitive impairment (HIV-MCMD) (MSK 0.5–1) (n=20; 70% > mean+1SD), with moderate cognitive impairment (HIV-HAD) (MSK≥2) (n=17; 82.4% > mean+1SD), HIV negative controls (n=5), and neuro-inflammatory controls (n=8). Anti-Tat levels in spinal fluid of all HIV groups are significantly higher than in controls. The points in the figure represent individual patient data and lines represent the mean. Statistical analysis was by ANOVA, with Newman-Keuls post-test.