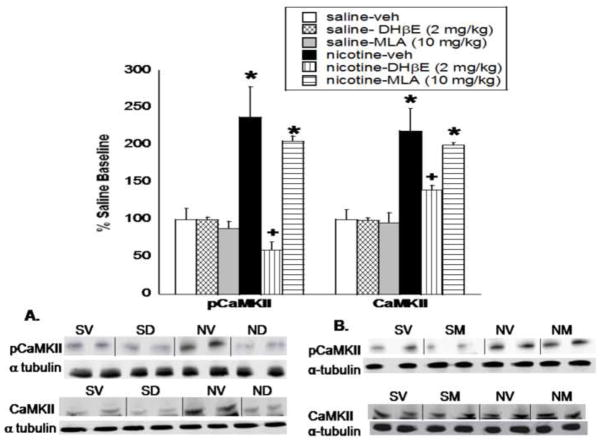
Fig. 1. DHβE, but not MLA, precipitates a reduction in CaMKII activity and protein level in the nucleus accumbens.
Mice were chronically infused with nicotine or saline for 14 days, and treated with vehicle, DHβE (2 mg/kg, s.c.) or MLA (10 mg/kg, s.c.) on the morning of day 15. Western blot analysis shows that CaMKII activity (pCaMKII) and total protein level (CaMKII) were significantly reduced in the nucleus accumbens after treatment with A. DHβE, but not B. MLA. Results from two independent blots were combined, normalized, and represented as a percentage of saline baseline. The x-axis represents the protein analyzed. the y-axis represents the percent expression compared to saline baseline. Each point represents the mean ± S.E.M of 4–8 mice per group. * denotes P < 0.05 vs. saline and nicotine-antagonist groups. + denotes P < 0.05 vs. chronic nicotine groups. veh, vehicle; SV, saline-vehicle; SD, saline-DHβE; SM, saline-MLA; NV, nicotine-vehicle; ND- nicotine-DHβE; NM-nicotine-MLA