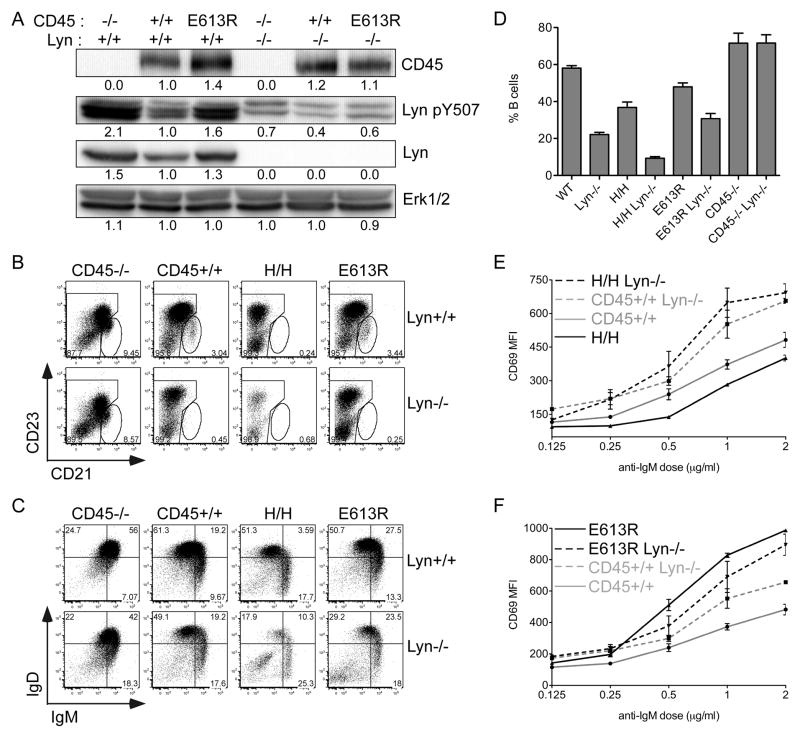
Figure 4. Lyn is required to mediate phenotype of H/H but not E613R B cells.
(A) Whole-cell lysates of resting B cells from E613R, +/+, and CD45−/− mice genetically sufficient or deficient for Lyn were blotted with Ab to the inhibitory tyrosine of Lyn (Lyn Y507). Total CD45, Lyn, and Erk1/2 are detected as loading controls.
(B, C) Representative plots of splenic B cells from E613R, +/+, CD45−/− and H/H mice genetically sufficient or deficient for Lyn stained to identify B cell developmental stages (MZ = CD21+CD23low splenic B cells; T1=IgMhiIgDlo; T2/3/FO=IgDhi).
(D) Graph representing % B cells in the spleens of mice from E613R, +/+, CD45−/− and H/H mice genetically sufficient or deficient for Lyn. Values are mean ± SEM of three biological replicates.
Data in 4B–D are representative of at least 3 biological replicates.
(E, F) Graph representing MFI of CD69 expression on LN B cells from E613R and allelic series mice genetically sufficient or deficient for Lyn stimulated for 16 hours with varying doses of anti-IgM. Values are mean ± SEM of three biological replicates. Data in 4B–F are representative of at least three independent experiments.