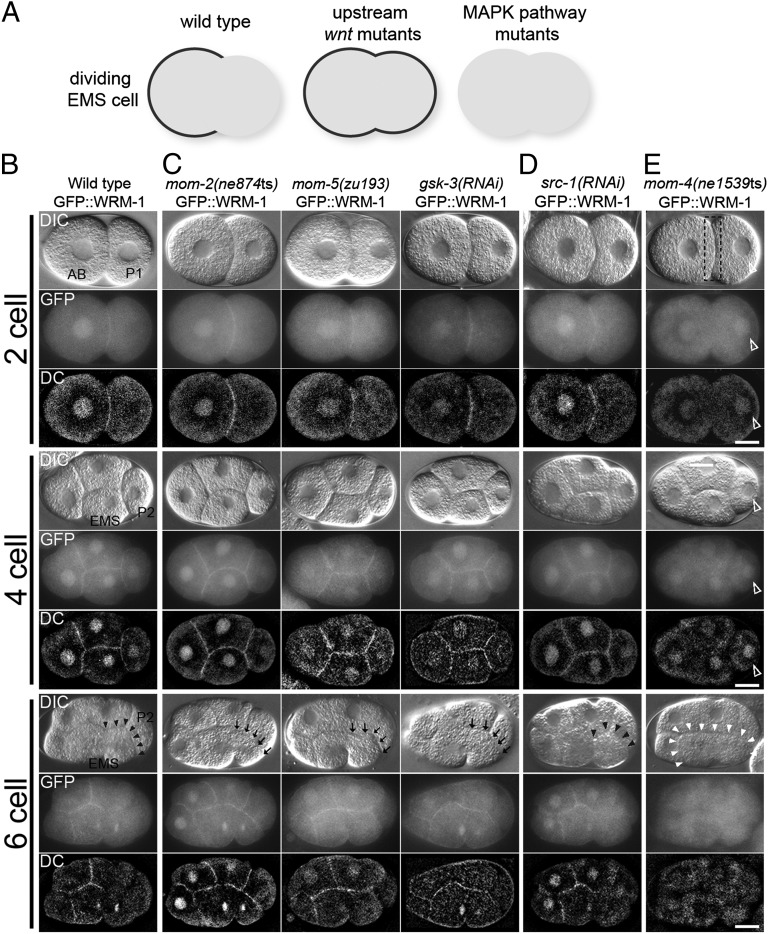
Fig. 1.
WRM-1 cortical localization is regulated by Wnt and MAPK-like pathways in early embryos. (A) A schematic representation of GFP::WRM-1 localization in dividing EMS cell in indicated genetic backgrounds. Cortical GFP signal is depicted by a thick black line. (B–E) Nomarsky (DIC), fluorescence (GFP), and deconvoluted fluorescence (DC) micrographs of two-, four-, and six-cell stages (or late four-cell stage) embryos expressing GFP::WRM-1 in (B) WT background, (C) upstream Wnt pathway mutants, (D) Src, and (E) MAPK-like pathway mutants indicated. Black arrowheads indicate absence of cortical WRM-1, and black arrows indicate retention of WRM-1 on the posterior EMS cortex. In E, white arrowheads indicate entire EMS cortex without cortical WRM-1 localization. Dotted box in two-cell stage indicates the absence of cortical WRM-1 at AB and P1 boundary, whereas empty arrowheads indicate ectopic accumulation of nuclear WRM-1 in P1 and P2 cells. Anterior is to the left, and dorsal is up. AB, P1, P2, and EMS cells are indicated in the WT DIC panels. (Scale bar: 10 μm.)