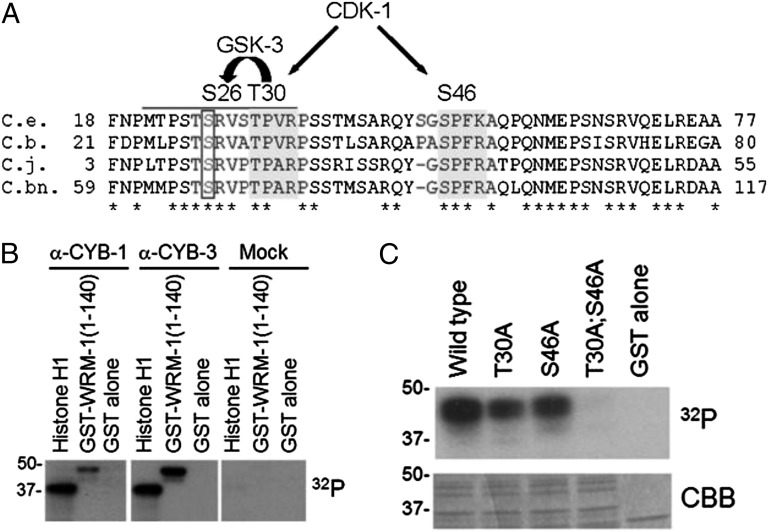
Fig. 3.
WRM-1 is phosphorylated by CDK-1 in vitro. (A) Amino acid alignments of an N-terminal region of WRM-1 from C. elegans (C.e.) and related nematodes C. briggsae (C.b.), C. japonica (C.j.), and C. brennei (C.bn.). Conserved CDK-1 consensus sites are highlighted in dark gray. Conserved GSK-3 site that is coupled to the CDK-1 site is boxed. Phosphoacceptor residues are indicated above the alignment. (B) In vitro phosphorylation of WRM-1(1-140) by CYB-1 (α-CYB-1), CYB-3 (α-CYB-3), or control (mock) immune complexes. Histone H1 is provided as a positive control substrate, and GST alone is provided as a negative control substrate. (C) In vitro phosphorylation of WRM-1(1-140) substrates by human recombinant CDC2/Cyclin B kinase. Mutations in CDK-1 phosphoacceptor residues are indicated. CBB, Coomassie Brilliant Blue.