Fig. P1.
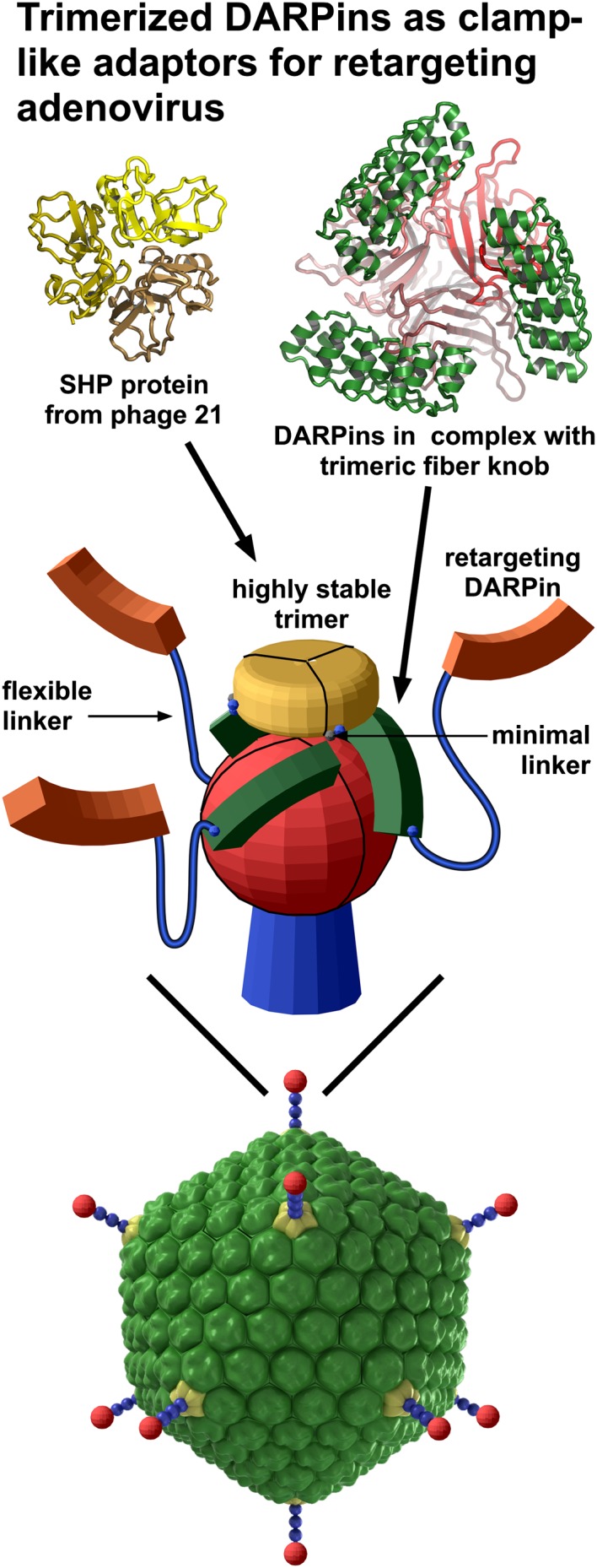
Strategy for developing a bispecific, trimeric, DARPin-based Ad adapter with high functional affinity and specificity. (Middle) The bispecific adapter contained a DARPin (green) selected by ribosome display to bind to the knob domain of the Ad fiber (red) and a retargeting DARPin (orange). The crystal structure of the DARPin (green) and knob (red) complex (Top Right) allowed the design of a stable trimeric clamp via fusion connected by a minimal linker to the lambdoid phage 21 coat protein SHP (yellow), for which the crystal structure (Top Left) previously had been determined. To create the adapter, the clamp was fused to a retargeting DARPin (orange) capable of recognizing a target cell-surface receptor via a flexible (G4S)4 linker (blue) (Middle). (Bottom) The Ad5 structure showing the major capsid proteins: hexon (green), penton base (yellow), and fiber, comprising the fiber shaft (blue) and the fiber knob domain (red).
