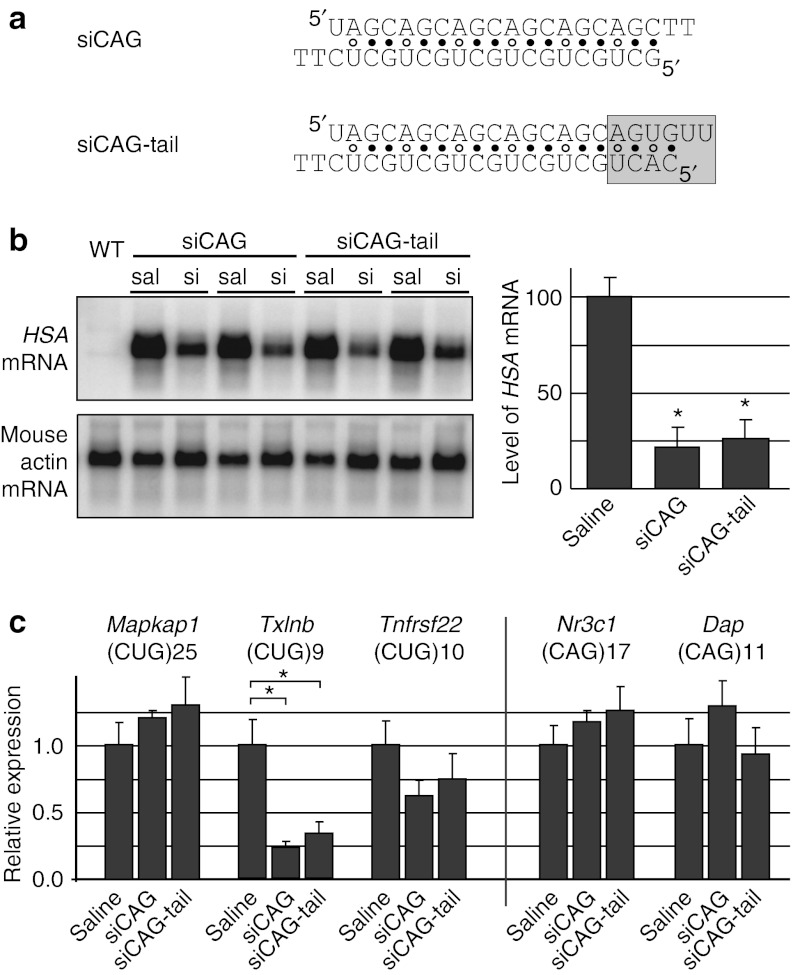
Figure 1.
siRNA directed against CUG repeats (siCAG) causes knockdown of CUGexp expression and reduction of nuclear RNA foci in mouse skeletal muscle in vivo. (a) Sequences of siRNAs used in this study; gray box shows the putative siRNA nuclear localization signal in the siCAG-tail duplex. (b) Northern blot for CUGexp transcript in RNA from tibialis anterior (TA) muscle. RNA was isolated 7 days after electroporation of siCAG or siCAG tail (si), as compared with saline-electroporation control (sal). Results were normalized to endogenous mouse Acta1 for quantification on graph (mean ± SD, at least four independent experiments, * denotes P < 0.0001, t-test). (c) qRT-PCR for endogenous transcripts containing CUG repeats (Mapkap1, Txlnb, and Tnfrsf22) or CAG repeats (Nr3c1 and Dap). The number of repeats in each transcript is indicated. TA muscle from human skeletal actin—long repeat (HSALR) mice was taken 7 days after electroporation of saline, siCAG or siCAG tail (n = 3 mice per each group, *P < 0.0001, t-test). Expression was normalized to Gtf2b, a housekeeping transcript that shows low variance in wild type or HSALR muscle.12 WT, wild type.