Figure 3.
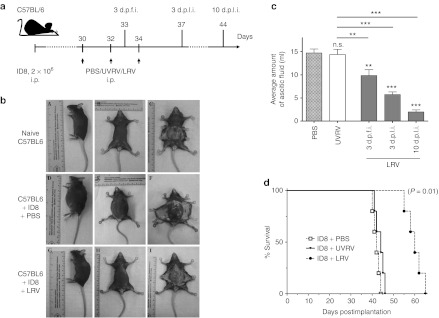
Virotherapy to target established advanced OC. (a) Female C57BL/6 mice were implanted i.p. with ID8 cells, injected with a regimen of PBS/UVRV/LRV as shown and then monitored for the (b) development of PC, (c) amount of ascitic fluid, and (d) survival. (b) Representative example of OC-PC–bearing animals treated with LRV against PBS-treated or non-OC–bearing animal. (c) Graphs represent volume of ascitic fluid collected from PBS/UVRV-treated animals on the day they were killed or LRV-treated animals on the days indicated. Data was analyzed with Student's t-tests at 95% CI; ns = P > 0.05; *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001. Statistics shown immediately on top of the bars was obtained by comparing the respective data against PBS control, while analysis above the horizontal lines were obtained through comparison of LRV-treated animals with that of UVRV-treated ones. (d) Survival in respective experimental groups (injected as per a) was calculated with the Kaplan–Meier survival method. The data is representative of three independent experiments. CI, confidence interval; d.p.f.i, days post first injection; d.p.l.i., days post last injection; i.p., intraperitoneally; LRV, live reovirus; ns, not significant; OC, ovarian cancer; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PC, peritoneal carcinomatosis; UVRV, UV-inactivated reovirus.
