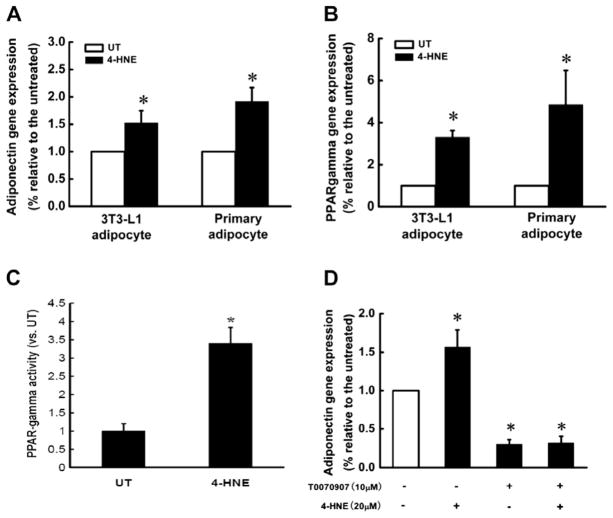
Fig. 3.
4-HNE increase adiponectin gene expressions in adipocytes via PPAR-γ activation. Fully differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes or mouse primary adipocytes were treated with 4-HNE (20 μM) for 16 h. Total RNA in each group was isolated to determine the gene expression of adiponectin and PPAR-γ via real time RT-PCR. (A) 4-HNE significantly increased adiponectin gene expressions in both 3T3-L1 and primary adipocytes. (B) 4-HNE significantly increased PPAR-γ gene expression in both 3T3-L1 and primary adipocytes. After exposure to 4-HNE (20 μM) for 16 h, the nuclear proteins in 3T3-L1 adipocytes were extracted and used for ELISA assay for PPAR-γ transactivity. (C) 4-HNE significantly increased PPAR-γ DNA binding activity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. After pretreatment with T0070907 (10 μM), a PPAR-γ antagonist, for 2 h, 3T3-L1 adipocytes were exposed to 4-HNE (20 μM) for 16 h and the total RNA in each group was isolated to determine the gene expression of adiponectin via real time RT-PCR. (D) Inhibition of PPAR-γ activation by T0070907 abolished 4-HNE-induced elevation of adiponectin expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Data are means ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05 when compared with the untreated group.