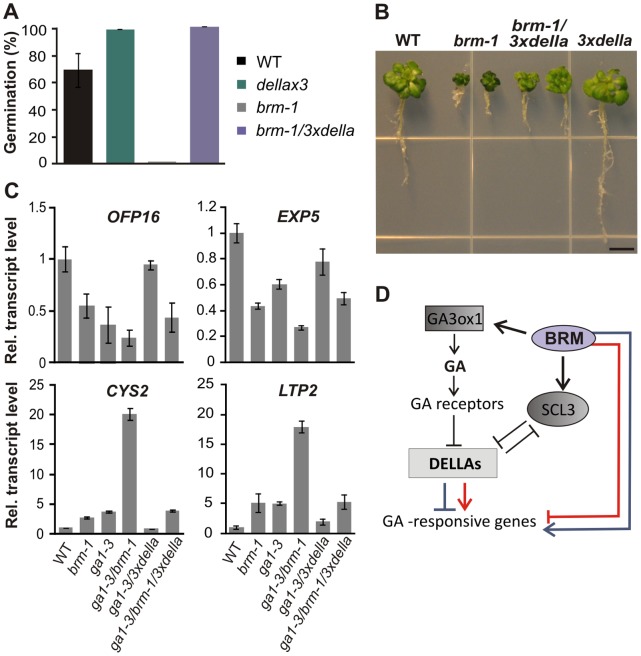
Figure 6. BRM acts through distinct mechanisms to regulate GA-mediated responses.
(A), Germination of the brm-1 mutant on 10 µM PAC is rescued by the triple della mutation. The progeny of brm-1/BRM plants were analyzed 10 days after sowing. (B), Phenotypes of 3-week-old plants grown on 2.5 µM PAC. The brm-1/3xdella line shows an intermediate growth phenotype. Bar = 5 mm. (C), RT-qPCR analysis of relative transcript levels of the OFP16, EXP5, CYS2 and LTP2 genes in 18-d-old wild type, brm-1, ga1-3, ga1-3/brm-1, ga1-3/3xdella and ga1-3/brm-1/3xdella lines. Transcript levels in the wild type were set to 1. Data are the means ± s.d. of 3 biological replicates. (D), Model of the role of BRM in regulating the expression of GA-responsive genes. BRM positively regulates the GA3ox1 and SCL3 genes involved in GA biosynthesis and signaling, and probably through this influences the expression of many GA-responsive genes in the opposite manner to DELLA repressors. In addition, BRM seems to act on a subset of GA-responsive genes independently of DELLA repressors. Also in this case, the effect exerted by BRM is typically in the opposite direction to that of DELLAs and is observed both for genes up- and down-regulated by the SWI/SNF complex (blue and red lines, respectively).