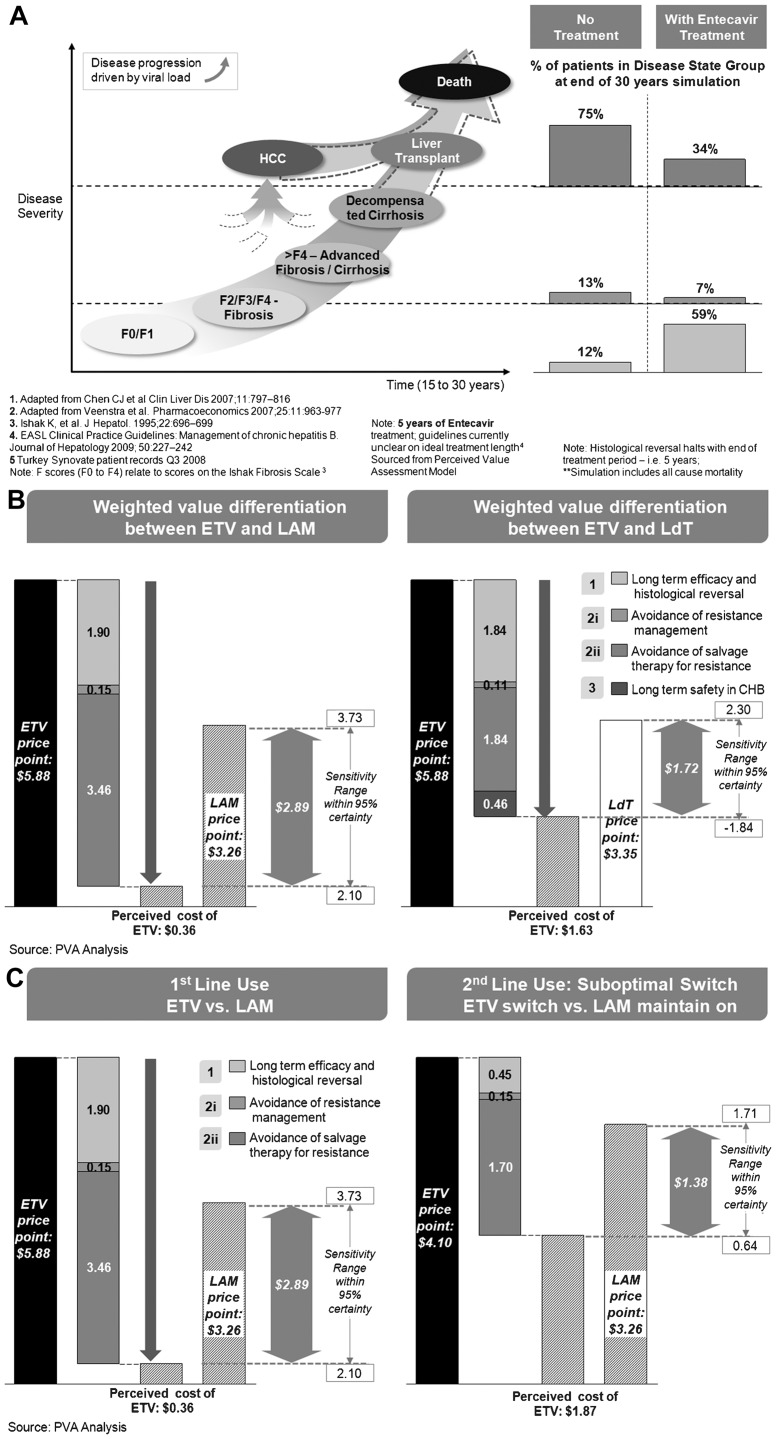
Figure 3. Model Output.
(A) Simulation of No treatment vs. treatment with entecavir for a Korean CHB population: Model simulation of patient outcomes at year 30 in two hypothetical Korean cohorts of patients with chronic hepatitis B, 60% of whom were HBeAg-positive. A total of 1000 patients were untreated and 1000 patients received entecavir treatment for 5 years (B) Weighted value differentiations between entecavir versus lamivudine or telbivudine: Daily cost savings per patient with chronic hepatitis B (60% with HBeAg-positive CHB) in Korea over a 30-year period by use of entecavir instead of lamivudine or telbivudine assuming an average patient lifespan of 65 years and an average initiation age of 35 years and 5 years of treatment with 74% compliance (histological reversal stops when treatment stops). Sensitivity analysis was conducted within 95% Confidence Interval. (C) Weighted value differentiations between switching to entecavir versus maintaining on lamivudine of suboptimal responders for lamivudine: Daily cost savings per patient with chronic hepatitis B (60% with HBeAg-positive CHB) in Korea over a 30-year period by use of entecavir instead of maintain on lamivudine assuming an average patient lifespan of 65 years and an average initiation age of 35 years and 5 years of treatment with 74% compliance (histological reversal stops when treatment stops). Sensitivity analysis was conducted within 95% Confidence Interval.