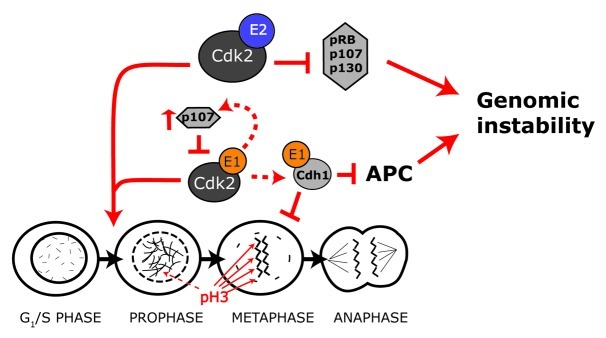
Figure 8. Model of cyclin E1 and E2 action. Both cyclin E1 and cyclin E2 promote G1-S phase progression. However they have different actions during mitosis. Cyclin E1 activates CDK2 to phosphorylate and stabilize Cdh1. This leads to inhibition of the APC and ultimately causes a metaphase delay and genomic instability. Cyclin E1 overexpression also upregulates p107, leading to negative feedback on cyclin E1/CDK2 activity. In contrast cyclin E2 overexpression does not lead to Cdh1 stabilization, metaphase delay or increased levels of p107. In the absence of increased p107 expression, deregulated cyclin E2-CDK2 actvity leads to functional inactivation of pocket proteins and genomic instability.
