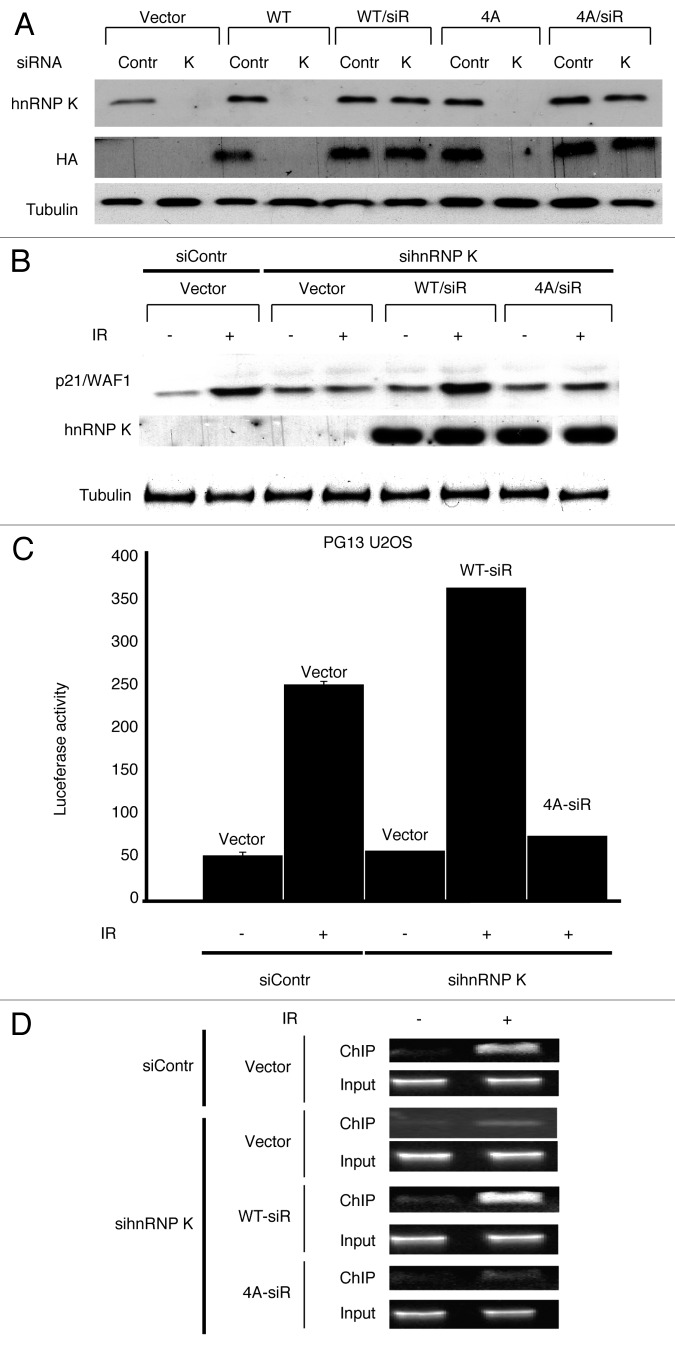
Figure 3. ATM-dependent phosphorylation of hnRNP K promotes p53 transcriptional activity following IR. (A) Expression from hnRNP K constructs was assessed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies in cells treated or not with control siRNA (Contr) or hnRNP K siRNA (K). As indicated, these cells also contained control parental vector (Vector), or constructs expressing wild-type hnRNP (WT), siRNA resistant wild-type hnRNP K (WT/siR), 4A mutant hnRN K (4A) or siRNA resistant 4A hnRNP K (4A/siR). Anti-tubulin antibody was used as loading control. (B) p53-dependent induction of p21/WAF1 protein was assessed 6 h following IR by western blotting in cells treated with the indicated siRNAs and containing the indicated constructs. (C) U2OS cells stably transfected with a luciferase reporter gene under the control of multiple p53 binding sites (PG13 U2OS) were transfected with the indicated constructs and then IR (15 Gy) treated or mock IR treated, as indicated. Luciferase activity was measured 18 h afterwards. (D) U2OS cells were transfected with the indicated constructs, treated with control of hnRNP K siRNAs and 48 h later, they were mock treated or exposed to IR (15 Gy) and incubated for 2 h. Samples were then subjected to ChIP with anti-p53 antibody, and precipitated DNA was subjected to PCR with primers covering the p53-response elements of the p21/WAF1 promoter.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.