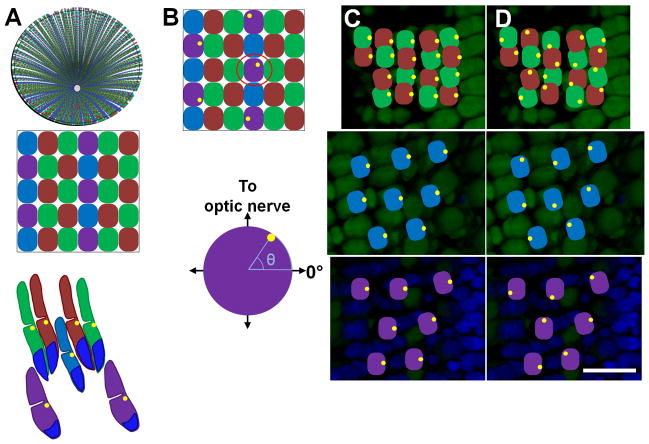
Figure 1. Basal body positioning within the zebrafish cone mosaic.
(A) Top: Schematic of an adult retina showing the cone row mosaic radiating out from the optic nerve. Middle: Magnification (below) shows the mosaic pattern of the red- (R), green- (G), blue- (B), and UV- (U) sensitive cones. Bottom: Schematic of the vertical tiering of cones within the photoreceptor layer. Basal bodies (yellow dots) are located in the ellipsoids at the base of the outer segments. Nuclei are labeled in blue. (B) Top: Schematic with basal bodies in the UV-sensitive cones adopting a random distribution around the perimeter of the cell. Bottom: The angular position of a basal body in one selected UV-sensitive cone (below) is determined as shown. (C) Fluorescent image of an oblique cryosection through a retinal flatmount. Photoreceptor nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Autofluorescence (green) from excitation with 488 nm light shows inner and outer segments. (D–E) Potential basal body arrangements for red-/green-sensitive cones (top panels), blue-sensitive cones (middle panels), and UV-sensitive cones (bottom panels) at their appropriate depths in the retina are illustrated. Basal bodies may be asymmetrically polarized and similarly positioned or are randomly positioned at the apical end of the inner segment. Basal bodies are illustrated in yellow. Scale bar = 10 μm. Magenta-green copies are available in the Journal’s supplemental data figures.