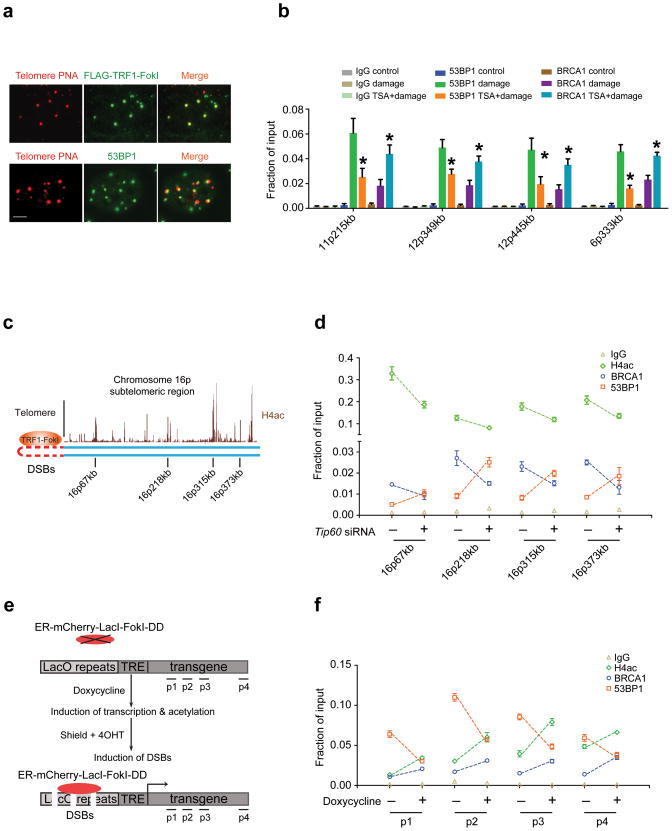
Figure 2. DNA damage and transcription dependent acetylation regulates BRCA1 and 53BP1 DSB occupancy.
(a) TRF1-FokI colocalizes with telomeres and 53BP1 foci are observed adjacent to telomeric signals as shown by immuno-FISH using peptide nucleic acid probes against telomeres (Telomere PNA). Scale bar, 10 μm. (b) ChIP using antibodies to BRCA1 and 53BP1 at different subtelomeric regions in 293T cells with (Damage) or without (Control) expression of TRF1-FokI. Treatment with TSA is indicated. The chromosome location and distance from the telomere is indicated at each qPCR primer set. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (S.E.M). * indicates p<0.05. (c) Schematic of the subtelomeric region of 16p denoting histone H4ac pattern (UCSC genome browser) and positions of ChIP-qPCR primer sets. (d) ChIP was performed at regions of high H4ac as indicated in c in 293T cells expressing TRF1-FokI following transfection of control or TIP60 siRNA. (e) Schematic of DSB induction in transcriptionally inactive or active chromatin. Transcription is induced with doxycycline prior to DSB induction. (f) ChIP was performed in the presence or absence of doxycycline as described in e. Induction of DSBs by mCherry-LacI-FokI was included in all conditions tested following the addition of doxycycline. Error bars represent S.E.M. * indicates p<0.05.