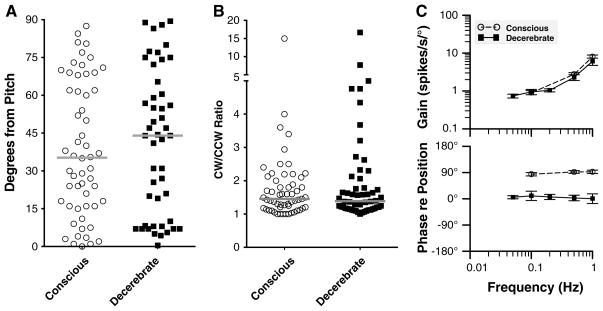
Fig. 6.
Comparisons of the responses of LTF neurons to vertical plane tilts in conscious animals (obtained in this study) with those collected in decerebrate animals (from Moy et al. 2012). Open circles and filled squares, respectively, show data from conscious and decerebrate animals. a Comparison of the axis of the response vector orientation in the two preparations. The axis direction is indicated relative to the pitch plane, such that a value of 90° indicates a response vector orientation aligned with the roll plane. Gray bars designate median values. b Comparison of the relative gains of responses to CW and CCW wobble stimuli delivered at 0.5 Hz for each neuron. To facilitate comparisons, the larger gain was always used as the numerator, and the smaller as the denominator, so the ratio for each unit was ≥1. Gray bars designate median values. c Average Bode plots for all neurons. Response gain and phase were plotted with respect to stimulus position. Error bars designate one SEM