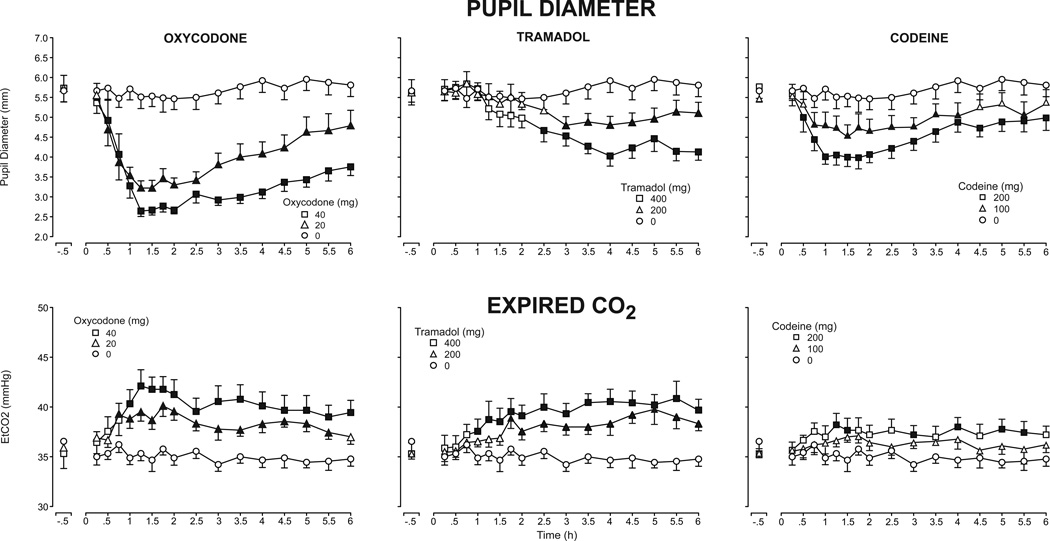
Figure 1.
Mean pupil diameter (top panel) and expired CO2 (bottom panel) after administration of oxycodone (left column), tramadol (middle column) and codeine (right column) as a function of time following drug administration across the 6-hour session (n=9, ±1 SEM). Time course analysis revealed a significant effect of dose on pupil diameter (F[6,48]=14.79, p<.001), and Dunnett post-hoc tests indicated both doses of oxycodone and the high doses of tramadol and codeine decreased pupil diameter relative to placebo (p<.05). A main effect of dose was also detected on expired CO2 concentrations (F[6,48]=7.98, p<.001), with a significant effect of both oxycodone and tramadol doses and 200 mg codeine on expired CO2, relative to placebo (Dunnett post-hoc, p<.05). Filled symbols indicate means that were significantly different from placebo at a particular time point (Dunnett post-hoc, p<.05).