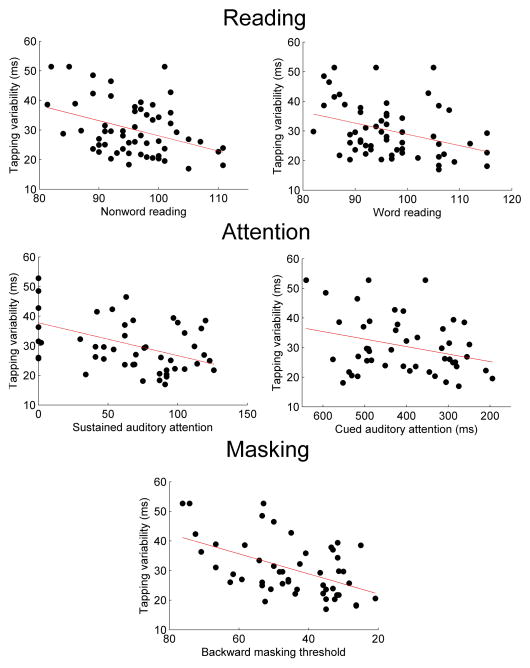
Figure 1.
The variability of subjects’ tapping to a beat (composite paced condition) correlates with performance on tests of reading (Woodcock-Johnson Test of Achievement), attention, and the ability to detect a stimulus in the presence of a masking sound (no gap condition). Each x-axis is arranged such that better performance is to the right.