Figure 3. A schematic representation of signaling pathways known to regulate pol III transcription in S.cerevisiae.
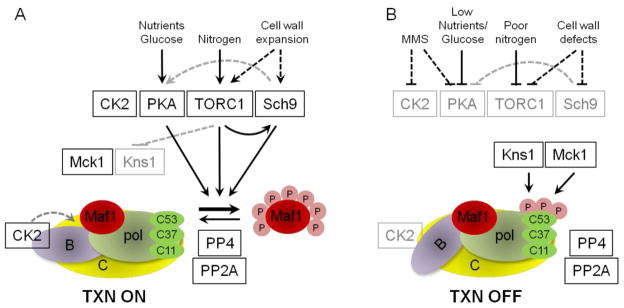
A. Transcription by pol III is sensitive to inputs from multiple signaling pathways that sense nutrients, glucose and cell wall expansion. In logarithmically growing cells in nutrient replete media the activities of PKA, TORC1 and CK2 promote transcription. CK2 activity is required for pol III transcription through a mechanism that affects TFIIIB activity. The Tpk, Sch9 and TORC1 kinases negatively regulate the repressor of pol III, Maf1, by phosphorylation at its seven PKA/Sch9-consensus sites. It is not known if there is preferential modification of specific sites in vivo by either enzyme. CK2 also promotes Maf1 phosphorylation at PKA/Sch9 sites through an unknown mechanism. Maf1 is dephosphorylated by the phosphatases PP4 and PP2A. Dotted lines indicate that the mechanism of inhibition is either not completely defined or is not direct. Black boxes indicate active enzymes while gray boxes indicate in inactive enzymes. Phosphorylation is indicated by the pink circles (annotated P); and the transcription components TFIIIC, yellow; pol III, light green; Rpc53/37/11 pol subunits, dark green; TFIIIB, purple and Maf1, red. B. Pol III transcription is shut-down in response to cellular stress. Maf1 is dephosphorylated and binds pol III in a manner that interferes with the C82/34/31 subcomplex, function in transcription initiation and binding to TFIIIB. Actively transcribing and reinitiating pol III is unaffected by Maf1. Cell stress and loss of transcription correlate with phosphorylation of Rpc53 and activation of the Kns1 kinase. Kns1 primes the pol III subunit Rpc53 for further phosphorylation by Mck1 in response to stress signaling pathways. Phosphorylation of Rpc53 occurs independently of Maf1 and Maf1 is not phosphorylated by Kns1 or Mck1. CK2 activity is impaired by DNA damage by a mechanism that promotes the dissociation of the catalytic subunits from TFIIIB. See section 3.6.1 for details.
