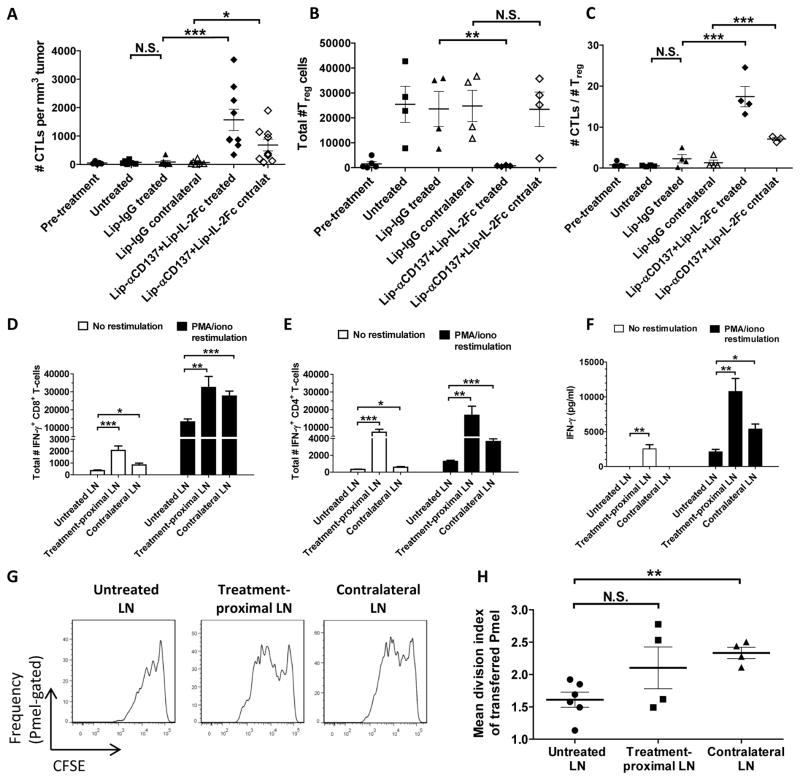
Figure 7.
Lip-αCD137 + Lip-IL-2Fc therapy induces immune activation at treated and distal B16F10 tumors and tumor-draining LNs. A–F. Dual-tumor-bearing mice were treated i.t. on one flank with PBS, control Lip-IgG, or Lip-αCD137+Lip-IL-2Fc on days 9 and 12 post-inoculation. On day 15, treated (filled symbols) and contralateral untreated (open symbols) tumors were analyzed by flow cytometry to determine numbers of tumor-infiltrating CTLs (A, *p=0.03, ***p=0.007), Tregs (B, **p=0.02), and CTL:Treg ratios (C, ***p=0.001). On day 14, cells from treatment-proximal and contralateral tumor-draining LNs were cultured ex vivo for 12h with or without PMA/ionomycin restimulation, and IFN-γ-producing CD8+ (D) and CD4+ T-cells (E) were enumerated by intracellular cytokine staining; *p=0.02, **p<0.01, ***p<0.003. Culture supernatants were analyzed by ELISA for secreted IFN-γ (F); *p=0.002, **p<0.001. G–H. Dual-tumor-bearing mice received an adoptive transfer of 2×106 naïve CFSE-labeled Pmel-1 CD8+ T-cells on day 7, then were treated on days 9+12 as above. CFSE dilution in Pmel-1 cells from TDLNs was analyzed on day 14 by flow cytometry (G), and mean division indices (mean divisions per cell) were calculated (H); **p=0.002.