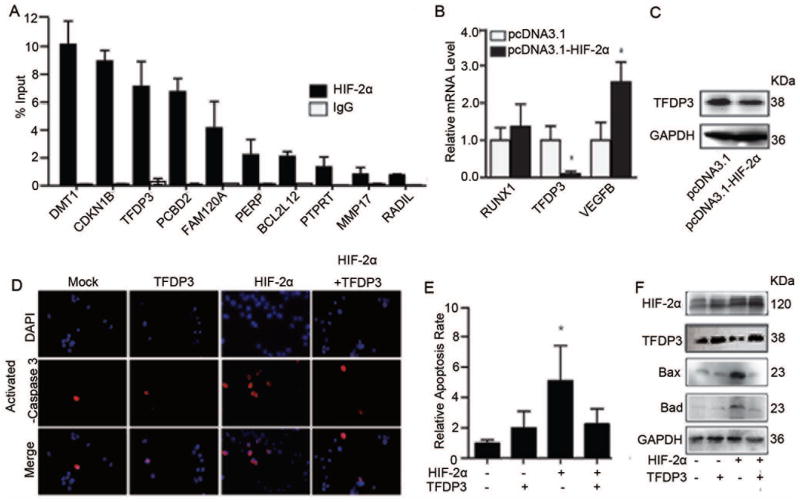
Figure 4.
HIF-2α augments cell apoptosis by inhibiting the target gene TFDP3 expression. (A) HIF-2α target genes identified by ChIP-on-chip were further validation by ChIP-PCR. The fold change of HIF-2α content in immunoprecipitates over the input are presented; error bars indicate standard deviation (SD). (B) Relative expression of apoptosis genes in representative monoclonal cells that were stably transfected with empty vector or recombinant HIF-2α expression plasmid (n=3). *, p<0.05, two-tailed test. (C) TFDP3 and GAPDH protein expression in representative monoclonal stable cell lines transfected with empty vector (pcDNA3.1) or recombinant HIF-2α expression plasmid (pcDNA3.1-HIF-2α). (D) Transient expression of HIF-2α by transfection of pcDNA3.1-HIF-2α or TFDP3 (pcDNA3.1-TFDP3) versus control empty vector (pcDNA3.1) in MHCC97H cells. Anti-activated caspase-3 antibody was used to test the rate of apoptosis in each group. (E) Quantification of the relative percentage of activated caspase 3-positive cells relative to varying expression levels of HIF-2α and TFDP3. *, p<0.05. (F) The expression levels of Bax and Bad were determined, and HIF-2α and TFDP3 levels were also confirmed in cells that were transiently transfected with HIF-2α or TFDP3 expression plasmids.