Figure 1.
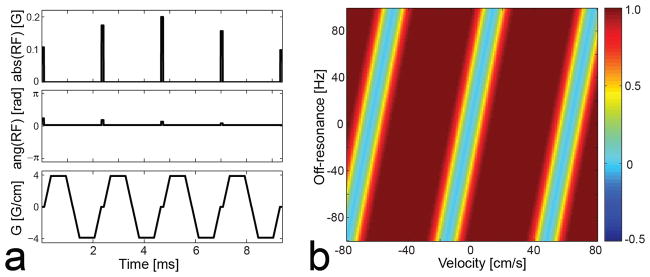
Reference VS saturation pulse sequence designed based on the excitation k-space formalism (a) and simulated longitudinal magnetization Mz over the v-f plane (b). In the figure of simulated Mz, a positive velocity indicates flow moving inferiorly (i.e., the direction of arterial flow in the legs). On resonance, the VS sequence saturates magnetization moving at 0 to 4 cm/s in the superior direction, which includes stationary tissues and venous blood, but barely affects magnetization moving at 10 to 50 cm/s in the inferior direction, which includes arterial blood at a peak systolic phase. However, the Mz profile is shifted along velocity in proportion to off-resonance (0.15 cm/s/Hz), which potentially degrades artery-to-background contrast.
