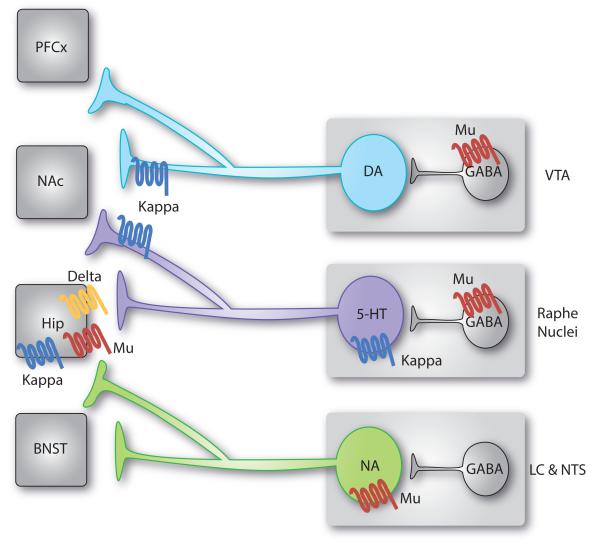
Figure 3. Functional interactions between opioid receptors and monoaminergic systems relevant to mood control.
Monoaminergic neurons synthesizing dopamine (DA), serotonin (5-HT) and nordrenaline (NA) originate in the brainstem and send axonal projections throughout the whole brain. These neurons are regulated by opioid receptors at multiple sites. Represented here are main receptor pools, where functional effects have been documented or proposed in the context of mood-related behaviors (see text for details). Other receptor populations may also contribute. In summary, activation of mu opioid receptors (MORs) expressed in the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) by local GABAergic interneurons disinhibit 5-HT [67-70] and DA [1] neurons. On the contrary, noradrenergic neurons are directly inhibited by MORs [83]. Chronic morphine treatment targets MORs in all these regions. Acute withdrawal from chronic morphine produces conditioned place aversion (CPA), which relies on increased activity of noradrenergic neurons targeting the bed nucleus of stria terminalis (BNST) [83]. Prolonged withdrawal from chronic morphine, or abstinence, leads to 5-HT dysfunction and progressive depressive-like behaviours [75, 76]. Kappa opioid receptors (KORs) expressed presynaptically in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) by 5-HT neurons are sufficient for KOR-induced CPA [80]. In addition, stress potentiates the activity of the dynorphin/KOR system, which targets both (i) DA neurons (and possibly 5-HT neurons) in the NAc to produce depressive-like behaviours [27], and (ii) 5-HT neurons in the DRN to mediate acute social avoidance [81]. Finally, evidence suggests that additional receptor populations are likely to be implicated in mood regulation: all 3 opioid receptors modulate BDNF activity and neurogenesis in the hippocampus (Hipp) [88], and KORs selectively control DA neurons projecting to the prefrontal cortex (PFC) [27].