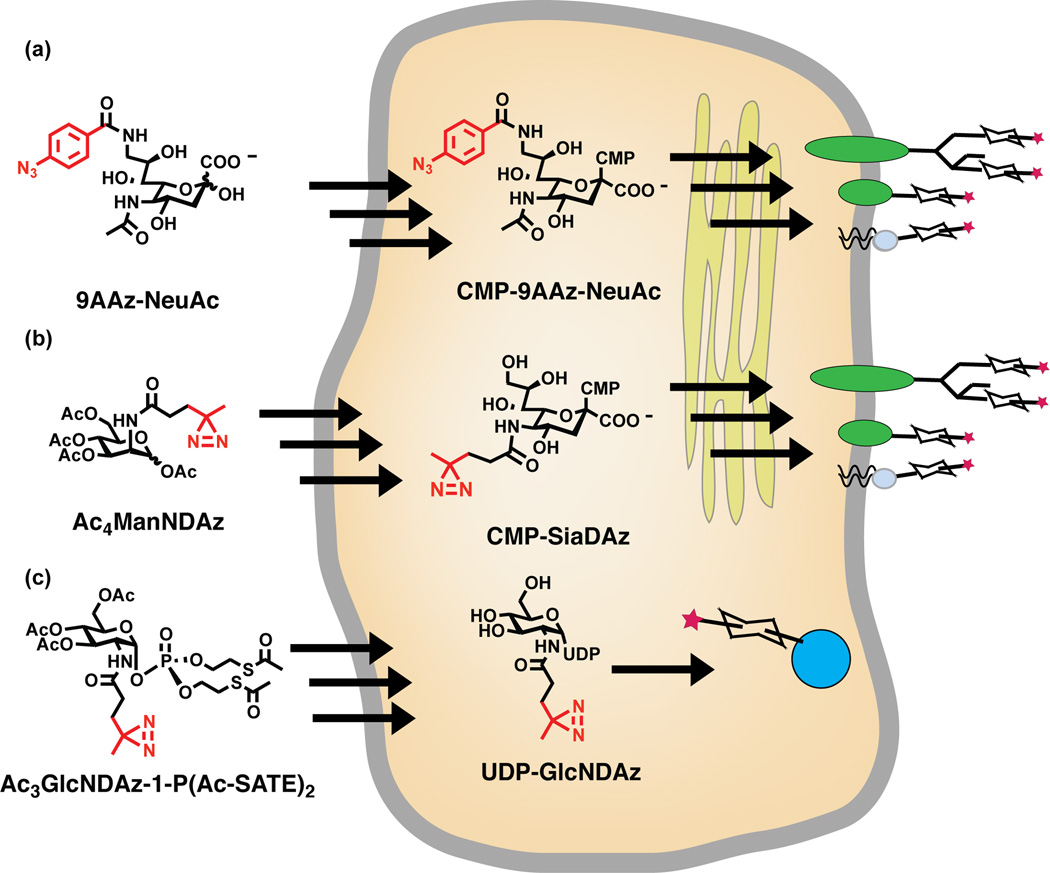
Figure 2. Metabolic incorporation of photocrosslinking sugars.
(a) 9AAzNeuAc is a photocrosslinking analog of sialic acid. The aryl azide crosslinker is shown in red. Cells are cultured with 9AAzNeuAc, which enters cells and is activated to CMP-9AAzNeuAc by endogenous enzymes. CMP-9AAzNeuAc is transported into the secretory pathway where endogenous sialyltransferases transfer 9AAzNeuAc onto glycoproteins. Although there is currently no direct evidence, it is likely that 9AAzNeuAc is also transferred onto glycolipids. (b) SiaDAz is another photocrosslinking analog of sialic acid. The alkyl diazirine crosslinker is shown in red. Cells cultured with a cell-permeable precursor to SiaDAz, Ac4ManNDAz, use endogenous enzymes to metabolize this compound to CMP-SiaDAz. CMP-SiaDAz is transported into the secretory pathway where endogenous sialyltransferases transfer SiaDAz to glycoproteins and glycolipids. (c) GlcNDAz is a photocrosslinking analog of GlcNAc, containing an alkyl diazirine photocrosslinker (red). Cells are cultured with a cell-permeable analog of GlcNDAz-1-P, which is converted to UDP-GlcNDAz by intracellular enzymes. The endogenous O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) transfers GlcNDAz to serines and threonines of nucleocytoplasmic proteins. More detail given in Figure 5.