Figure 1. XID mice exhibit enhanced survival and control of SchuS4 replication compared to WT mice.
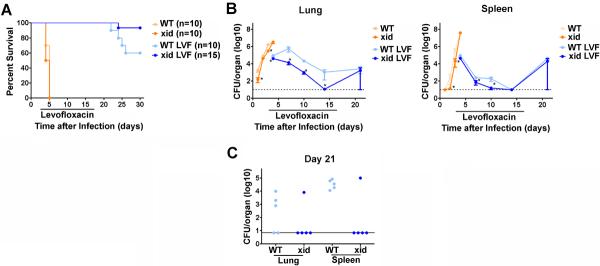
Mice were intranasally infected with 50 CFU F. tularensis strain SchuS4. As indicated, animals received 5 mg/kg levofloxacin (LVF) on days 3–16 of infection. CBA/J (WT) and CBA/CaHN-BtkXID/J (XID) mice were monitored for survival (A) or euthanized at the indicated time points for assessment of bacterial loads in the lung and spleen (B and C; n=4–5 mice/group/time point). (A) represents the results of two experiments pooled together. (B) is representative of two experiments of similar design. * = significantly less than WT mice (p<0.05). Error bars represent SEM.
